Organizational activities that provide a pool of applicants for the purpose of filling job openings is Recruitment. It is a process of searching for prospective employees. Stimulating and encouraging them to apply for jobs in the organization. It brings together employer and employee.
Table of Contents
Sources of Recruitment
Attracting and choosing the most qualified applicants for open positions is known as recruitment. Companies can hire from within (internal recruitment) or outside (external recruitment), each strategy with pros and cons of its own.
Sources of Recruiting within the Organization
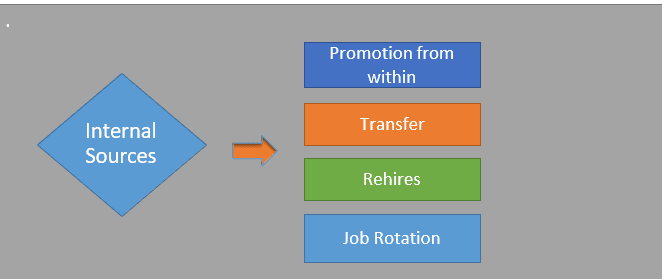
Advantages of Internal Recruitment
- We Already Know Internal Candidates.
- In-House Recruitment Costs Less to Hire
- Internal Candidates Already Know the Company
- Internal Candidates Are Easier to Find
- In-House Recruitment Boosts Company Loyalty and Engagement
- Hiring Internally Reduces Hire Time
Disadvantages of Internal Recruiting
- Limited Choice: It does not tap any candidate from outside the organization.
- Favouritism: There will be tendency of referring friends and family members in the organization.
- Costly: When one employee is promoted or transferred, his/her position will be vacant and another employee is to be recruited.
- No Opportunity: New and fresh talents do not get opportunity.
- Seniority-based: Recruitment are based on seniority, not on merit.
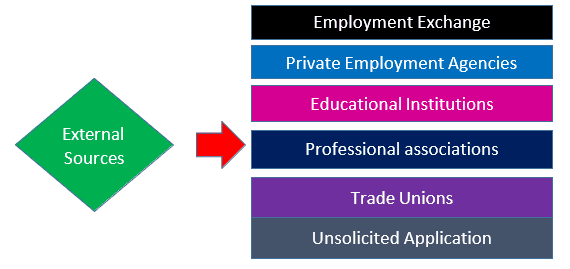
External Sources of Recruitment (Recruiting Outside the Organization)
What is Raiding or Poaching?
A practice that involves an employer contacting an employee at a competing company with the intention of convincing the employee to apply for a job at their company.
Advantages
- Wider Choice: With the availability of large pool of candidate, the selection process becomes more competitive.
- Fresh and Qualified Personnel: It provides a sufficiently large pool of qualified and fresh talents for selection purpose.
- Fairness: Being an open process, there is no favouritism and nepotism in external recruiting.
- Environmental Adaptation: Since it encourages the entry of new skills, knowledge and ideas in the organization, it helps in accompanying environment changes.
Disadvantages
- Expensive: It requires an extra cost for vacancy announcement, arrangement of employment office, employee training etc.
- Dissatisfaction: When the qualified employees are recruited from out side the organization, the existing employees may feel dissatisfied with their job.
- Adaptability Problems: More time will be needed for new employees to be familiar with organizational arrangement.
- Wrong Selection: Since new employees are not already known, the chances of selecting wrong candidate will be high.
Protected Class
A group of individuals possessing some common characteristics who are safeguarded from discrimination in employment on the basis of those characteristics. Protected classes are usually created by the government of the country.
Discrimination is the act of excluding a person or categories of people based on their protected status. Hiring only men, for example, discriminates against women.
Followings are included in Protected classes:- Race, Color, Religion, Age, Gender, Pregnancy, Citizenship etc.
Recruitment of Protected Class
- Provide equal employment opportunity to people of the nation
- A mandatory act or voluntary rule of participating all differently able, minority, backward society in recruitment.
- Also known as inclusiveness in recruitment
- Protected class recruitment contains the following two aspects.
- Equal employment opportunity (EEO)
- Affirmative action plan (AAP)
Equal Employment Opportunity
Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) refers to government efforts to prevent discrimination and ensure fair treatment during the hiring and management of employees. It ensures that employers do not discriminate against individuals based on race, color, religion, sex, age, disability, or any other personal characteristics in the recruitment process. The goal of EEO is to provide all individuals with an equal chance to compete for jobs, promotions, and career advancements without facing bias or unfair treatment.
In the context of Industrial Policy 2065 (which is based on the Nepali calendar, corresponding to the year 2008-09 in the Gregorian calendar), the provisions focus on promoting fairness and non-discrimination in the workplace. It emphasizes policies that ensure every worker has equal rights and access to opportunities, aiming to create a diverse and inclusive workforce. The policy aligns with the broader global movement towards inclusivity and equality, fostering a more equitable labor market and reducing barriers that marginalized groups may face in the workplace.
Affirmative Action Plan
Affirmative Action is a proactive program designed to ensure equality of opportunity for members of historically underrepresented groups, including people of color, women, individuals with disabilities etc. Main objective is to remedy past and current discrimination. It makes special provisions to recruit, train, promote or grant some other benefits to members of protected class or groups, may be beyond the EEO provision. It is mandatory and should be followed by the concerned types of organization.
Electronic Recruitment
The Electronic Recruitment also called as Online Recruitment or E-Recruitment is the process of hiring the potential candidates for the vacant job positions, using the electronic resources, particularly the internet. E-Recruitment includes the entire process of finding the prospective candidates, assessing, interviewing and hiring them, as per the job requirement.

Advantages of E-Recruitment
- Low cost per candidate, as compared to the physical recruitment process.
- Wide geographical coverage, i.e. the candidates can be hired from any part of the world.
- Less time required in hiring the potential candidate for the firm.
- Right people for the right job can be easily found through E- Recruitment, by matching the candidate’s CVs with the job profile.
- The recruitment process becomes more efficient and easy to record details of the applicant.
Employee Selection
A process of examining the applicants with regard to their suitability for the given job, and choosing best from the suitable candidates and rejecting the others.
The selection process is a series of steps used to decide which applicants should be hired.

Selection Process
Application Form Evaluation
Applications received from different individuals are evaluated to access whether they have met the specifications mentioned earlier. Consist of information about- personal background information, qualification, work experience, expected salary and reference.
Preliminary Interview
- Very short interview and centers on job requirement.
- Objective is to screened out unqualified and unsuitable candidates.
Selection Tests
- Used to access the ability, aptitude and personality of prospective candidates.
- Types of test can be: intelligence test, aptitude test, interest test, personality test, achievement test etc.
Final Interview (Selection Interview)
- Face to face observation of candidate’s suitability for the job and related to job description and job specifications.
- Objective is to seek more reliable and factual information about the candidate and to find out suitability of candidate in performing organizational act.
Reference Check
The names mentioned as referees are contracted to confirm the candidate’s work record and appraisal of his performance. Previous character of the candidate is checked.
Physical Examination
- Screens out those candidates who are not mentally and physically fit for the work.
- Approved physician conducts drug testing and fitness testing.
Hiring Decision
An appointment letter is issued.
Matching Person and Job
“Matching person with job” refers to aligning an individual’s cognitive abilities, interests, and personality traits with the requirements necessary for success in a particular role. This involves matching the knowledge, skills, and abilities of employees with the characteristics of the job, such as tasks, duties, and responsibilities. This process is typically done during the placement stage of an employee, ensuring that they are assigned to roles where they are most likely to succeed, feel engaged, and perform effectively, ultimately benefiting both the employee and the organization.
Why should we match person and job?
Effective job matching leads to several positive outcomes for both employees and the organization. It helps reduce employee turnover, absenteeism, and workplace accidents by ensuring that employees are well-suited to their roles. This alignment also improves employee morale and job satisfaction, as employees feel more competent and engaged in their work. Additionally, job matching enables better adjustment to the job and the work environment, allowing employees to thrive in their roles. Ultimately, when the right person is matched with the right job, it becomes the key to superior performance, benefiting both the individual and the organization.
Sources of Information About Job Candidates
Application Form
An official document that employers want their job candidates to fill in while applying for a job.
Consists of information about personal background information, qualification, work experience, salary etc.
Biographical Information Blanks
A self-report instrument that includes questions about past personal and work experiences, as well as interests, opinions, values, and attitudes.
Interviews
A face to face observation and appraisal of the candidate’s suitability for the job.
Helps to find out candidate’s GK, personality and personal skills, ability to work under pressure, level of motivation etc.
Tests
A practice of administering written, oral or other tests as a means of determining the suitability of the applicants.
Help to find out aptitude for the job, past achievement, personality dimensions etc.
Background Investigations
Process of determining whether an applicant may be unqualified for a position due to a record of criminal conviction, motor vehicle violations, poor credit history, or misrepresentation regarding education or work history.
Polygraph Honesty Tests
Lie detector test to measure honesty of the candidate
They ensure accuracy of information provided by the candidate.
Medical Examination
Approved physician conducts physical examination
Information about candidate’s fitness, suffering from contagious diseases, physical handicaps etc can be collected.
Employment Interview
A face to face interaction, between interviewee and interviewer. Used to evaluate the candidate’s suitability for the job and to secure maximum amount of information that can not be obtained from other methods. Tries to appraise an individual’s educational qualifications, training, family background, and other special proficiencies. A most important selection tool.
Purposes of Employment Interview
- Information: To seek more information about candidate
- Understanding and Confidence: To develop mutual understanding and to find out the level of confidence.
- Suitability: To find out suitability of the candidate for the job
- Job Description: To give the candidates clear picture of job
- Selection: To select efficient able and qualified personnel.
Types of Interview
Unstructured Interview
Questions are not planned in advance. They are made up during the interview.
Structured Interview
All the questions to be asked are planned in advance. Every candidates are asked the same questions. Has high validity and reliability.
Semi-structured Interview
Major question to be asked are broadly planned in advance. Interviewer has flexibility in asking other some specific questions also.
Some Interview Questions
- Why do you want to work with us?
- What do you know about us?
- Why should I hire you?
- What are your strengths and weaknesses?
- What can we expect from you?
- How can you contribute if you are selected?
- Why did you leave your last job?
- What is your expected salary? Etc.
Employment Test
A test taken by the employer for potential employees to see whether they are fit for the job profile being offered. Measures individual differences in a scientific manner and enable the recruiter to pick up qualified applicants in an unbiased manner. Can be in various forms such as written, oral, physical or even on the job tests.
Advantages of Employment Test
- Avoids biasness in selection procedure.
- Helps to minimize the cost and time to be taken by selection procedure.
- Provides a guideline for reference evaluation.
- Helps to estimate about the candidate’s ability and knowledge.
- Compares different candidates on the basis of skill, knowledge and special abilities possessed by them.
- Provides a basis for selecting the most likely candidate as per the requirement.
Types of Employment Tests
Aptitude Test
Measures an individual’s ability to learn, as well as to perform a job.
Achievement Test
A test given to measure skill or knowledge in a certain defined subject.
Intelligence Test
A test given to measure general ability for intellectual performance
Measures IQ (Intelligence Quotient) in terms of reasoning, numbers, memory etc.
Interest Test
Measures a candidate’s activity preference.
Attitudes Test
Used to measure the degree of positive or negative feeling associated with any slogan, person, institution, product and service etc.
Projective Test
A psychological tool designed to reveal a person’s unconscious thoughts, emotions and attitudes.
Honesty Test
A test given to measure accuracy of information provided by the candidate. Polygraph Test is an example of honesty test.
Situational Test
Candidates are asked to respond to the situation specific problem.
Group discussion is an example of such test.
Reaching a Selection Decision
Last step of selection process which is concerned with making final employment decision after passing all the selection hurdles. A step of employee selection in which the applicant is formally appointed for placement. Appointed candidate’s first placement is for a probation period, usually extending from 6 months to 12 months. During probation period, if the employee is found unsuitable, he/she may be transferred, or trained or suspended from the job opportunity.
Factors to be Considered Before Reaching a Selection Decision
- Relevant experience
- Education
- Salary requirement
- Geographical location
- •Legal requirements
Gender Issues in Recruitment and Selection
Any issue or concern determined by gender-based and/or sex-based differences between women and men. Gender bias in recruitment is the inclination to favor a candidate due to gender prejudice. A huge issue in hiring and can sadly affect all stages of the recruitment process.
Issues
- Not hiring a specific gender due to stereotypes and unconscious bias, i.e., not hiring a female applicant because you believe men are stronger leaders, more analytical, and more confident.
- Not providing all genders with the same opportunities to develop and progress i.e., training, mentoring, or promotional advances.
- Delegating tasks based on a person’s gender and perceived strengths.
- Verbal, physical, or sexual harassment.
- Hostile remarks made about people of a certain sexual orientation or gender identity.
- Not offering equal pay to both of the gender.
- Being held to different standards because of someone’s gender or sexual orientation.
- Being rejected for a position or forced to go on leave because someone is pregnant.
Induction
Induction: The task of introducing the new employee to the policies, procedure, rules and regulation of the organization.
Induction Program: A program conducted by the organization to provide new employee information about-
Organization: history, current position, rules, policies etc.
Employee benefits: pay scale, holidays, insurance, provident fund etc.
Working culture: introduction to superiors, co-workers, other key staffs etc.
Job duties: job location, job tasks, its relation with other jobs.
Objectives of Induction Program
- Welcome the new employees
- Remove fears of new employees
- Create a good impression
- Act as a valuable source of information
- Communicate to new employees what is expected of them, their responsibilities, and how they should handle themselves.
Placement
The process of placing an employee involves assigning them to a specific job, which includes defining their rank, responsibilities, and ensuring that their qualifications match the job requirements is Placement. New employees are allocated to roles initially on a probationary basis, typically lasting 6 to 12 months. During this probation period, their performance and suitability for the role are evaluated. Upon successful completion of the probationary period, the employee is given a permanent posting, solidifying their position within the organization.
Benefits of Proper Placement
Placing the right person in the right job is essential for the success of an organization, as it ensures that employees’ skills and abilities align with job requirements. This leads to the growth of the enterprise, as well as the optimum utilization of human resources. When employees are well-matched to their roles, it helps the organization stay competitive in the market. Additionally, it improves job satisfaction and employee morale, fostering a positive work environment. This strategic placement is key to the effectiveness of other HR functions, such as training, development, and performance management. As a result, it can also reduce employee turnover, absenteeism, and accidents, contributing to a more stable and productive workforce.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Recruitment?
The process of attracting and encouraging people to apply for job openings is Recruitment.
What is a Protected Class?
Groups protected from discrimination, e.g., based on race, gender, or disability.
What is an Affirmative Action Plan (AAP)?
A proactive effort to promote equal opportunities for underrepresented groups is Affirmative Action Plan.

