Telecommunication and Network are the systems and technology that make it possible for information to be shared across long distances. Transmitting data, sound, and video through cables, satellites, and wireless systems is known as telecommunication. Data transport, resource sharing, and internet connectivity are made possible via networks, which are interconnected systems like Local Area Networks (LAN) and Wide Area Networks (WAN). The foundation of contemporary communication and information sharing is made up of these.
Table of Contents
Networking the Enterprise
- Businesses are becoming networked enterprise. The internet, Intranet, extranet and other types of networks have become primary information technology infrastructure of many organization.
- An enterprise network is an enterprise’s communications backbone that helps connect computer and related devices across departments and workgroup networks, facilitating insight and data accessibility.
- The key purpose of an enterprise network is to eliminate isolated user and workgroup so that all systems should be able to communicate and provide and retrieve information.
- An enterprise network can integrate all systems, including windows, Apple computers, Operating systems, Unix Systems, Mainframes and related devices Like Smart Phones and tablets.
The Concept of a Network
- A network is common term referring to set of related elements or entities linked to each other.
- A computer network is a group of computer systems and other computing hardware devices that are linked together through communication channels to facilitate communication and resource-sharing among a wide range of users.
- Computers on network may be linked through wire or wireless such as cables, telephone lines, radio waves, satellites, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or Infrared beams.
The Business Value of Telecommunication and Network
Telecommunication gives an organization the capability to move the information rapidly between distance locations and to provide ability for the employees, customers, and suppliers to collaborate from anywhere.
Telecommunication may provide these values through the following impacts:
- Time compression (Overcome time barriers): Enables firm to transmit raw data and information quickly and accurately between remote sites.
- Overcoming geographical dispersions (barriers): Enable an organization with geographically remote site to function, to a degree, as though these sites were a single unit.
- Restructuring Business relationship: makes it possible to create systems which restructure the interactions of people within firm as well as firm’s relationship with customer.
- Overcome cost barrier: Reduce the cost of more traditional means of communication. It reduce expensive business trips, allows customers, suppliers and employees to collaborate, thus improving the quality of decision reached.
Types of Telecommunications Networks
Basically classified into two different types: They are:
- On the basis of geographical region
- On the basis of Architecture
On the basis of Geographical Region
Local Area Network (LAN)
LAN is a telecommunication network that connects information processing devices within a limited physical area. These network cover area such as Classroom, Floor, Offices, Buildings, Manufacturing plants.
- LAN uses various telecommunication media such as telephone wiring, twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, wireless radio system.
- LAN’s allows end user in workgroup to communicate electronically, share hardware, software and data resources.
- Simple and economical networks.
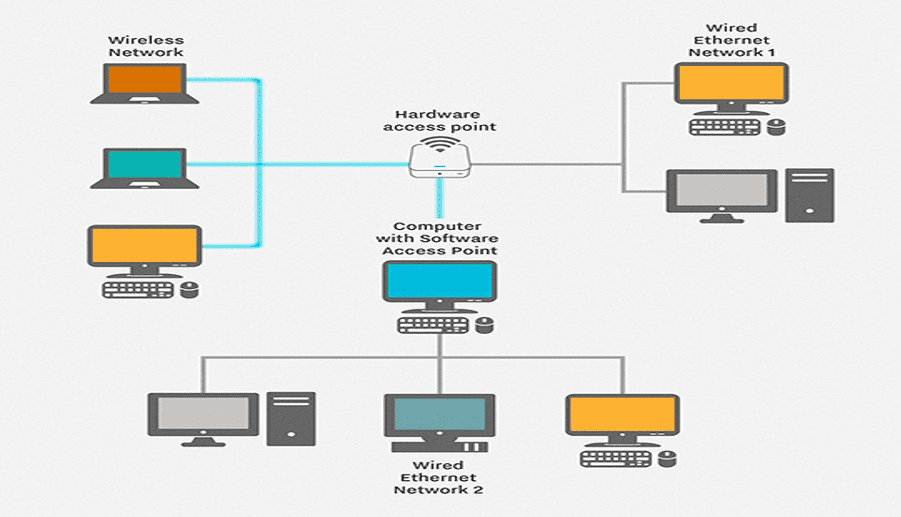
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- MAN is a telecommunication network that interconnects various LANs within a metropolitan area.
- Similar technology to LAN and similar speed.
- Coaxial cable is used.
- It is privately owned by owner or company.
- E.g. TV channel
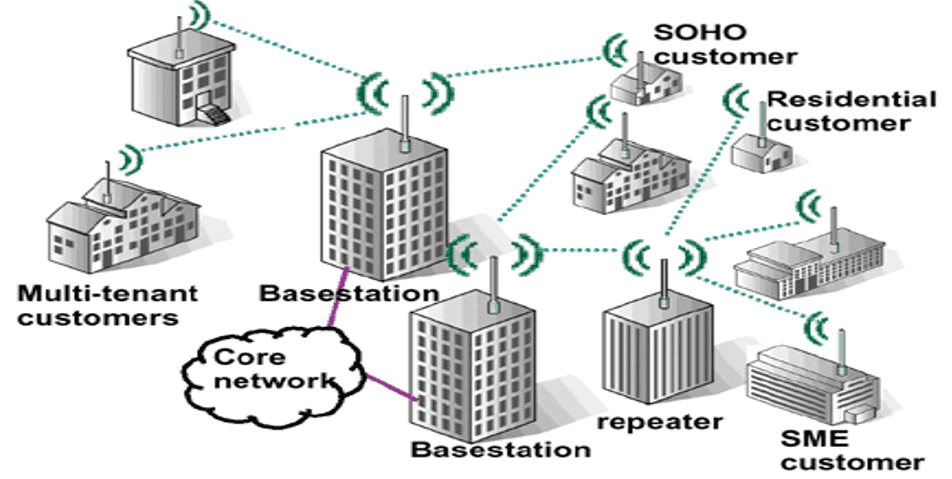
Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Wan is a telecommunications network that covers a large geographical areas. These networks cover areas such as:
- Large city or metropolitan area, whole country, Many countries and continents.
- Generally wireless technologies and wire (fiber optic is used in WAN)
- Different protocols are used
- It is slower than LAN and MAN
- Internet is an example.
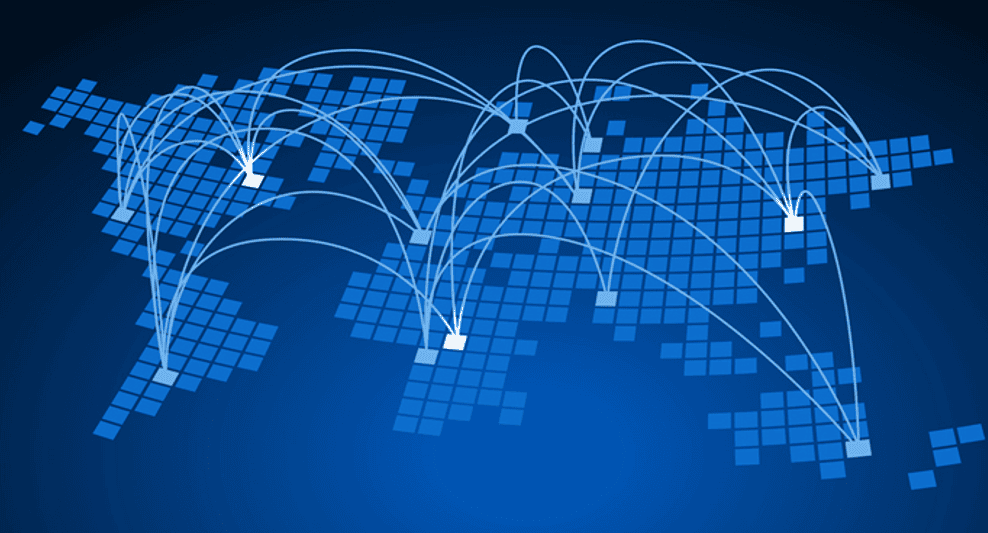

On the basis of architecture
Peer to peer Network (P2P)
- Peers are computer system which are connected to each other via the Network.
- Files can be directly shared between systems on the network without the need of a central server. i.e. every computer acts as client and server.
- The only requirement for P2P network is network and P2P software and can simply be connected using twisted pair cable.
- It has no privacy and security of the data in this system.
Client Server Network
- A network in which at least one computer acts as a server and other computers act as clients.
- Files and resources are centralized and is stored on server.
- If server is turned off its resources are not available.
- Advantage of client server network is that security is created, managed, and can highly get enforced.
- Centralized backup, intranet and internet monitoring are advantages of this network.
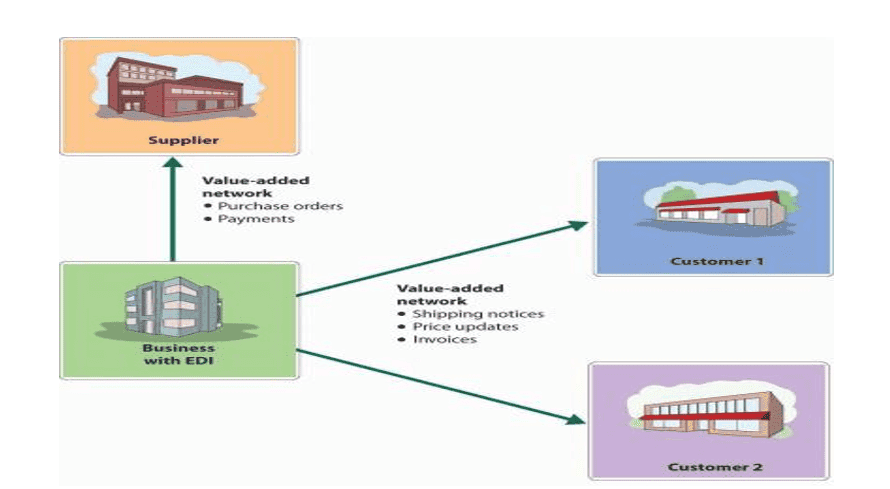
Value Added Network (VAN)
- A value- added network is a private network provider that is hired by a company to facilitate electronic data interchange (EDI) or provide other network services.
- The VAN acts as intermediary between business partners that share standards based or proprietary data.
- They were widely used by companies to transfer data before the introduction of WWW.
- Due to increase of E- Commerce EDI remains important part of business and still rely on VANs.
Telecommunication Links (Media)
Telecommunication links can be implemented with various communication media which can be wire or wireless.
Different potential media are employed to implement telecommunication links:
- Twisted pair
- Coaxial cable
- Fiber optics cable
- Terrestrial Microwave
- Satellite transmission
- Radio transmission
Twisted Pair Cable
- It is wired communication medium consisting a pair of wires twisted each other.
- Two primary types of twisted pair cable industry standard are defined- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP).
- It is simple, economic , enough data transfer speed and mostly used cable in LAN.
- The optimum data transfer is upto 100m.
Coaxial Cable
- It is a guided medium that consists of a relatively thick central conductor shielded by several layers of insulation and the second conductor shielded by several layers of insulation and the second conductor just under the protective cable’s shell.
- It is much less susceptible to interference and can carry much more data.
- Coaxial cable are connected and split using metal connectors known as T- Pieces.
Fiber Optic Cable
- It is a guided high speed communications medium that consists of many strands of pure glass with a data carrying core in the middle, surrounded by a reflective coating and a protective sheath.
- The core of fiber optic cable is made of glass and signals are sent along the cable optically rather than electrically.
- Two primary types of fiber optic cable industry standards are defined- single mode and multimode.
Terrestrial Microwave
- It is unguided long distance telecommunications by means of microwave signals that travel on the surface of earth.
- Microwave can be used for point to point communication because their small wavelength allows conveniently- sized antennas to direct them in narrow beams, which can be pointed directly at receiving antenna.
- The microwave are limited to line of sight propagation.
- They cannot pass around hills or mountains.
- Traditional TV broadcasting is the example of microwaves.
Satellite Transmission
- It is a form of microwave transmission in which signal is transmitted by an earth station to a satellite which rebroadcast the signal to the receiving station.
- It provides communication links between various points on earth.
- Types of information that can be transferred include: television, telephone, radio, internet and military.
- In order for people to communicate over a long distance, a satellite must be used to redirect the signal.
Radio Transmission
- It is wireless communication technology that transmits voice or data over the air using lower frequency band than microwave.
- Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum longer than infrared light.
- Like all other electromagnetic spectrum they travel at the speed of light.
- The signal travel in up and down manner so that it can reach any place until the strengths of waves.
Network Topologies
Computer switches and terminals are interconnected by network links are collectively called nodes.
The arrangement of nodes and links in a network is called topology.
A variety of arrangement is possible each with its own advantages and drawbacks.
The different topologies mostly used in computer network are:
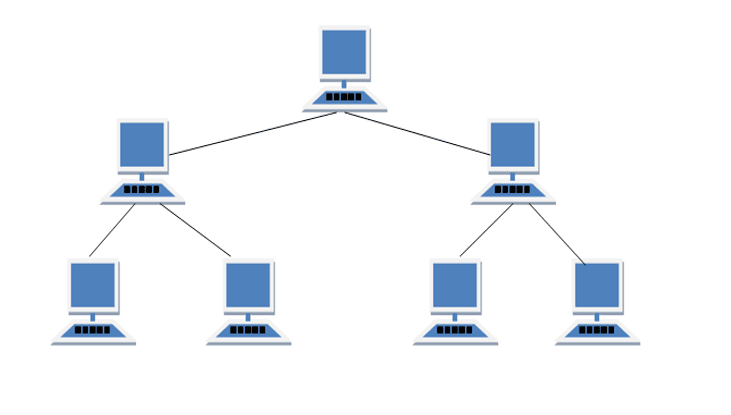
Hierarchical Topology
It has a root node and all other nodes are connected to it forming a hierarchy. It is also called hierarchical topology. It should at least have three levels to the hierarchy.
Features of Tree Topology :
- Ideal if workstations are located in groups.
- Used in Wide Area Network.
Advantages of Tree Topology :
- Extension of bus and star topologies.
- Expansion of nodes is possible and easy.
- Easily managed and maintained.
- Error detection is easily done.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology :
- Heavily cabled.
- Costly.
- If more nodes are added maintenance is difficult.
- Central hub fails, network fails.
Bus Topology
Bus topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to single cable. When it has exactly two endpoints, then it is called Linear Bus topology.
Features of Bus Topology :
- It transmits data only in one direction.
- Every device is connected to a single cable
Advantages of Bus Topology:
- It is cost effective.
- Cable required is least compared to other network topology.
- Used in small networks.
- It is easy to understand.
- Easy to expand joining two cables together.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology
- Cables fails then whole network fails.
- If network traffic is heavy or nodes are more the performance of the network decreases.
- Cable has a limited length.
- It is slower than the ring topology.

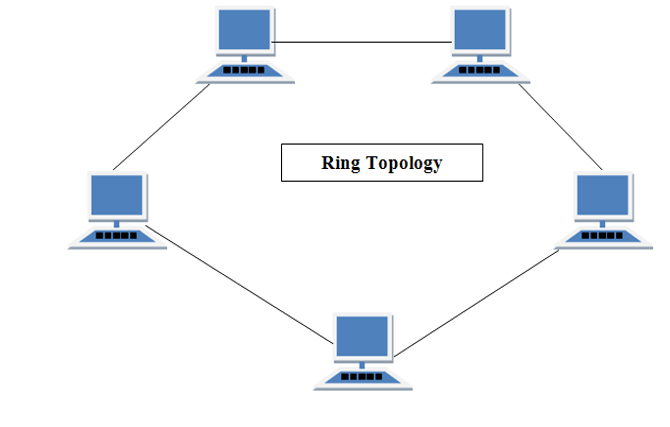
Ring Topology
It is called ring topology because it forms a ring as each computer is connected to another computer, with the last one connected to the first. Exactly two neighbours for each device.
Features of Ring Topology
- A number of repeaters are used for Ring topology with large number of nodes, because if someone wants to send some data to the last node in the ring topology with 100 nodes, then the data will have to pass through 99 nodes to reach the 100th node. Hence to prevent data loss repeaters are used in the network.
- The transmission is unidirectional, but it can be made bidirectional by having 2 connections between each Network Node, it is called Dual Ring Topology.
- In Dual Ring Topology, two ring networks are formed, and data flow is in opposite direction in them. Also, if one ring fails, the second ring can act as a backup, to keep the network up.
- Data is transferred in a sequential manner that is bit by bit. Data transmitted, has to pass through each node of the network, till the destination node.
Advantages of Ring Topology
- Transmitting network is not affected by high traffic or by adding more nodes, as only the nodes having tokens can transmit data.
- Cheap to install and expand
Disadvantages of Ring Topology
- Troubleshooting is difficult in ring topology.
- Adding or deleting the computers disturbs the network activity.
- Failure of one computer disturbs the whole network.
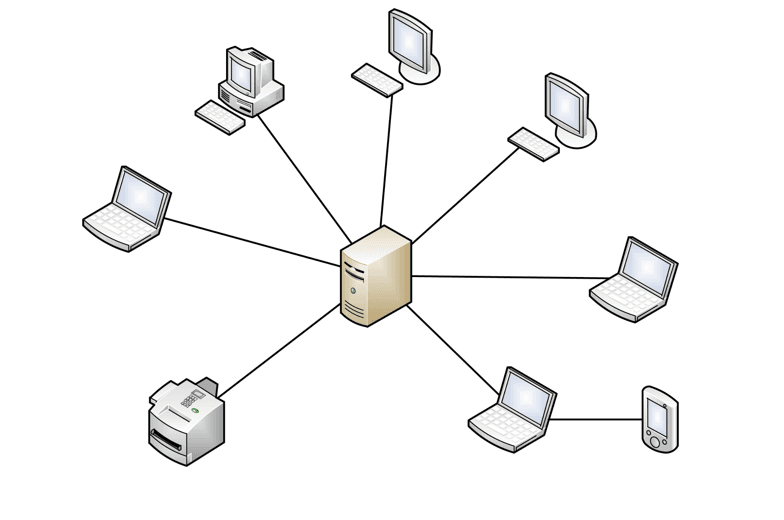
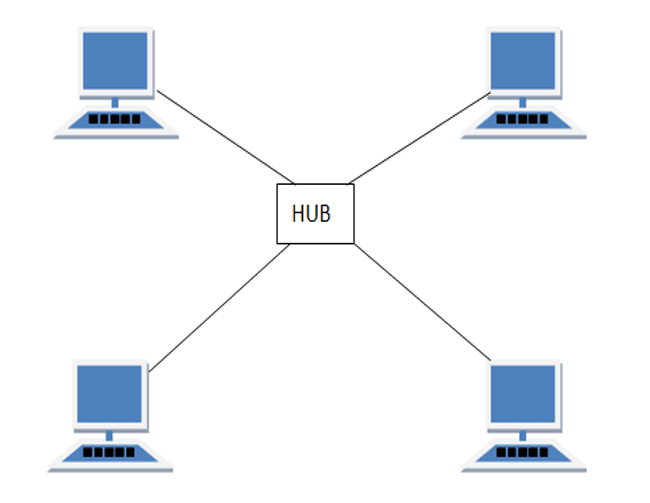
Star Topology
In this type of topology all the computers are connected to a single hub through a cable. This hub is the central node and all others nodes are connected to the central node.
Features of Star Topology
- Every node has its own dedicated connection to the hub.
- Hub acts as a repeater for data flow.
- Can be used with twisted pair, Optical Fibre or coaxial cable.
Advantages of Star Topology
- Fast performance with few nodes and low network traffic.
- Hub can be upgraded easily.
- Easy to troubleshoot.
- Easy to setup and modify.
- Only that node is affected which has failed, rest of the nodes can work smoothly.
Disadvantages of Star Topology
- Cost of installation is high.
- Expensive to use.
- If the hub fails then the whole network is stopped because all the nodes depend on the hub.
- Performance is based on the hub that is it depends on its capacity
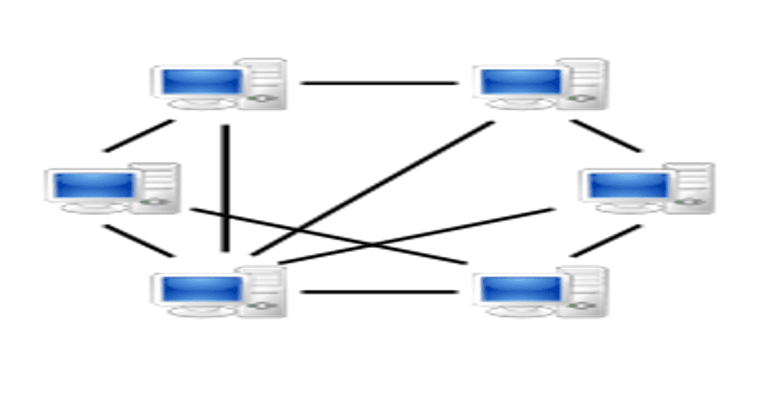
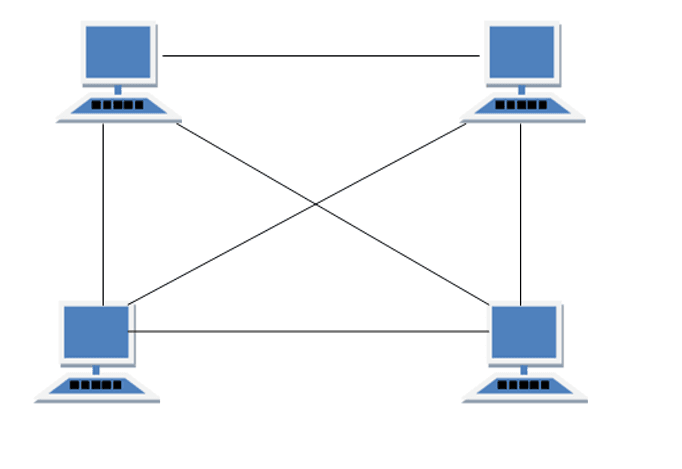
Mesh Topology
It is a point-to-point connection to other nodes or devices. All the network nodes are connected to each other. Mesh has n(n-2)/2 physical channels to link n devices.
There are two techniques to transmit data over the Mesh topology, they are :
- Routing
- Flooding
Routing
In routing, the nodes have a routing logic, as per the network requirements. Like routing logic to direct the data to reach the destination using the shortest distance.
Or, routing logic which has information about the broken links, and it avoids those node etc. We can even have routing logic, to re-configure the failed nodes.
Flooding
In flooding, the same data is transmitted to all the network nodes, hence no routing logic is required. The network is robust, and the its very unlikely to lose the data. But it leads to unwanted load over the network.
Features of Mesh Topology
- Fully connected.
- Robust.
- Not flexible.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
- Each connection can carry its own data load.
- It is robust.
- Fault is diagnosed easily.
- Provides security and privacy
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology
- Installation and configuration is difficult.
- Cabling cost is more.
- Bulk wiring is required.
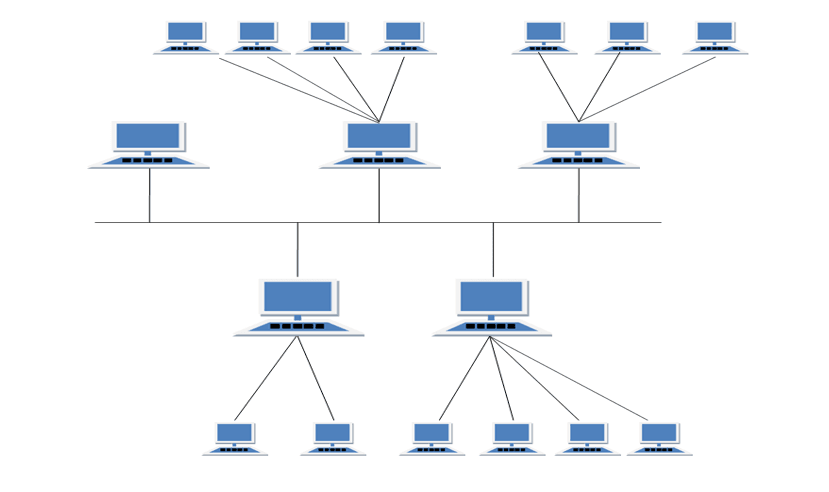
Hybrid Topology
It is two different types of topologies which is a mixture of two or more topologies. For example if in an office in one department ring topology is used and in another star topology is used, connecting these topologies will result in Hybrid Topology (ring topology and star topology).
Features of Hybrid Topology
- It is a combination of two or topologies
- Inherits the advantages and disadvantages of the topologies included
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
- Reliable as Error detecting and trouble shooting is easy.
- Effective.
- Scalable as size can be increased easily.
- Flexible.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
- Complex in design.
- Costly.
Trends in Telecommunication
Major trends in the field of telecommunications have a significant impact on management decisions in this area.
Industry Trend
- Telecommunication services are available from numerous large and small telecommunication companies.
- Growth of internet and WWW have created a host of a new telecommunication products, services and providers.
- Business firms have dramatically increased their use of the internet and the Web for electronic commerce and collaboration.
Technology Trends
- Using internet networking technologies as the technology platform, are becoming the primary telecommunication technology drivers.
- Increased industry and technical moves towards building Client/ Server networks based on Open system architecture.
- Change from analog to digital network technology.
- Change in communication media.
Business Application Trends
The trend toward more vendors, services, Internet technologies and open systems, Internet dramatically increased the number of feasible telecommunication applications.
Telecommunication networks are playing vital roles in electronic commerce, enterprise collaboration, and internal business application that support the operation, management and strategic objectives of both large and small companies.
Telecommunications functions have become an integral part of local and global computer networks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is telecommunication?
Technology such as cables, satellites, and wireless networks that are used to transmit data, voice, or video over long distances.
What is a network?
A network of linked computers, servers, and other devices that exchange information and resources.
What is the role of telecommunication in business?
It enables communication, data transfer, and remote collaboration, supporting efficient operations and decision-making.

