A Marketing Information System (MIS) is a structured framework that combines personnel, processes, technology, and tools to collect, process, analyze, store, and distribute data and information pertinent to marketing. This system is intended to support businesses in their marketing decision-making, ensuring that choices are well-informed, strategic, and consistent with the organization’s objectives. By transforming data into actionable insights, an MIS enables companies to effectively plan, execute, and assess their marketing initiatives.
Table of Contents
Relevance of Marketing Information System
In the contemporary marketing environment, marked by swift transformations and a growing dependence on data, the Marketing Information System (MIS) is of paramount importance. Its significance lies in its capacity to assist businesses in remaining competitive, agile, and focused on customer needs.
Enabling Informed Decision-Making
An MIS delivers precise, comprehensive, and real-time data that empowers marketers to make well-informed choices. These choices may encompass pricing strategies, promotional designs, product development, and the optimization of distribution channels.
Deepening Customer Insights
By conducting thorough analyses of customer data, an Marketing Information System aids businesses in acquiring profound insights into customer preferences, behaviors, and feedback. This knowledge facilitates the development of tailored marketing campaigns that resonate with target demographics, enhancing engagement and loyalty.
Tracking and Analyzing Market Dynamics
An MIS enables businesses to remain proactive by tracking market dynamics, customer demands, and competitor actions. This intelligence is crucial for adapting to market fluctuations, recognizing emerging opportunities, and sustaining a competitive advantage.
Enhancing Resource Allocation
By pinpointing effective marketing strategies and discarding ineffective ones, an Marketing Information System ensures the efficient distribution of marketing resources, including time, finances, and personnel. This approach results in improved returns on marketing investments.
Aiding Strategic Planning
With its capability to provide long-term insights, an Marketing Information System is instrumental in strategic marketing planning. It assists businesses in evaluating market potential, identifying growth avenues, and assessing risks, thereby establishing a robust foundation for enduring success.
Boosting Operational Efficiency
An MIS optimizes the processes of data collection, organization, and analysis, which reduces manual workloads, minimizes errors, and accelerates decision-making. This leads to enhanced efficiency in marketing operations.
Achieving Competitive Advantage
Organizations that proficiently leverage a Management Information System (MIS) secure a competitive advantage by maintaining enhanced awareness, demonstrating increased agility, and providing exceptional value to their customers. The capacity to foresee market fluctuations and react proactively enables them to stay ahead of their rivals.
Components of the Marketing Information System
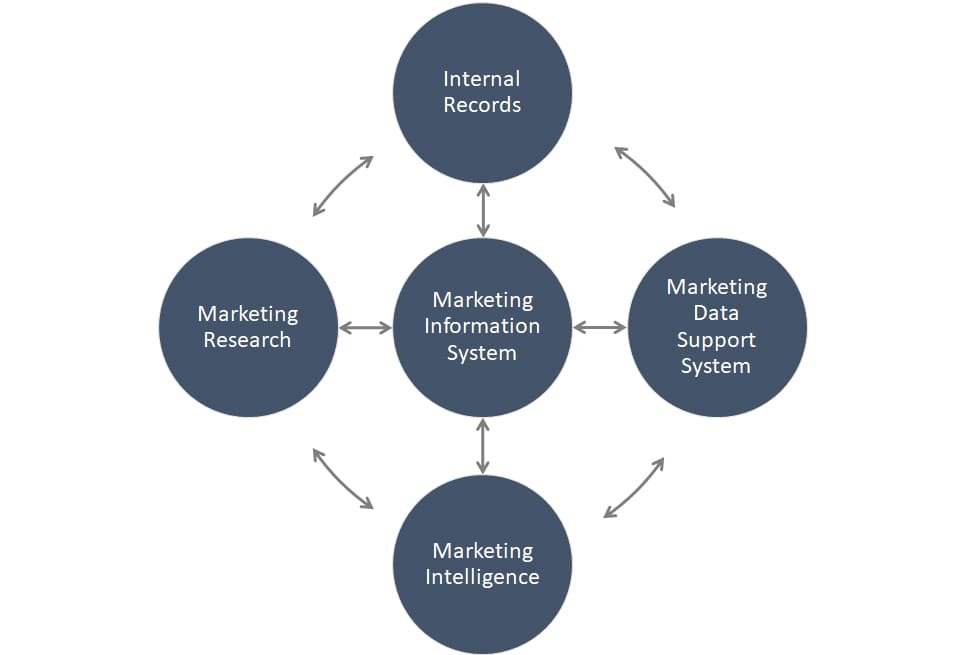
The Marketing Information System (MIS) comprises several essential components that collaborate to gather, process, analyze, and distribute marketing data. These elements are crucial for the effective operation of the system and offer significant insights to aid in decision-making. The primary components of an MIS are outlined below:
Internal Records System
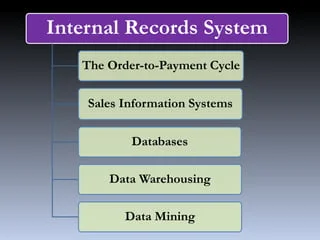
The Internal Records System entails the collection of data from within the organization to monitor its operations and performance. This component supplies both historical and real-time information regarding various facets of the business. Key data sources include:
- Sales Records: Data concerning sales volume, revenue, and product performance.
- Financial Reports: Information on costs, profits, and budget allocations.
- Customer Records: Details regarding customer transactions, purchase histories, and payment behaviors.
- Inventory Data: Information on stock levels, production schedules, and supply chain metrics.
This component enables managers to assess internal efficiency and identify trends or challenges.
Marketing Intelligence System
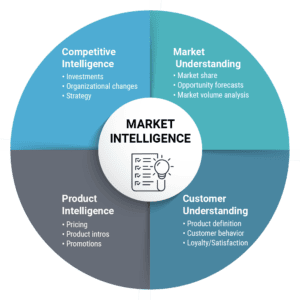
The Marketing Intelligence System is dedicated to collecting external data to comprehend the wider market landscape. This component ensures that the organization remains cognizant of external factors that may impact its operations. Key activities include:
- Monitoring competitor actions (e.g., pricing strategies, promotions, new product introductions).
- Tracking industry trends and market dynamics.
- Collecting insights on customer behavior and preferences through public data, social media, and industry reports.
- Staying updated on regulatory changes, economic conditions, and technological advancements.
This system provides businesses with actionable intelligence, enabling them to respond proactively to market changes.
Marketing Research System
The Marketing Research System entails the execution of customized research aimed at addressing particular marketing challenges or seizing opportunities. This element emphasizes the collection of primary data through:
- Surveys: To obtain customer opinions, preferences, and feedback.
- Focus Groups: To investigate consumer responses to products, services, or marketing strategies.
- Observation: To assess real-time consumer behavior in designated environments.
- Experiments: To evaluate hypotheses, such as the effects of varying pricing or packaging on sales.
- Marketing research yields comprehensive insights into consumer behavior, market demand, and potential opportunities.
Analytical Tools and Decision Support System
The Analytical Tools and Decision Support System is tasked with processing, analyzing, and interpreting the gathered data to produce insights. This component employs sophisticated tools and methodologies, including:
- Statistical Analysis: To uncover patterns, trends, and correlations within the data.
- Predictive Modeling: To anticipate future market trends, sales, or customer behavior.
- Data Visualization: To convey findings through charts, graphs, and dashboards for enhanced understanding.
- Software Solutions: Marketing automation platforms and decision-support tools that offer actionable recommendations.
- This component assists managers in transforming raw data into significant insights that inform strategic decisions.
Output and Reporting System
The Output and Reporting System represents the concluding component of the Management Information System (MIS), responsible for delivering processed data and insights to decision-makers. This component guarantees that the information is presented in a user-friendly and actionable format, such as:
- Regular reports (e.g., weekly, monthly, or quarterly).
- Dashboards displaying key performance indicators (KPIs).
- Alerts and notifications for significant changes or anomalies.
- This facilitates the timely distribution of insights, enabling prompt and informed decision-making.
Marketing Research Areas and Process
Marketing research is essential to the effective operation of the Marketing Information System (MIS). It offers valuable insights into particular marketing issues or opportunities, thereby enhancing the functionality of other data systems, including internal records and marketing intelligence. By systematically collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data, marketing research enables organizations to make well-informed and strategic decisions. The subsequent sections will detail the primary aspects of marketing research and its procedural relationship with MIS.
Marketing Research Areas
Marketing research encompasses several essential domains, each concentrating on distinct facets of marketing management. These domains empower organizations to acquire a comprehensive understanding of the market landscape, consumer behavior, competitive dynamics, and overall business efficacy.
Consumer Behavior
A pivotal domain within marketing research is consumer behavior. This domain investigates the psychological, social, and emotional elements that shape consumer decision-making processes. Researchers analyze the motivations behind consumer purchases, the criteria used to assess various products or services, and the influences that drive buying behavior. Gaining insights into consumer preferences, attitudes, and motivations enables marketers to refine their strategies and product offerings to align more closely with customer expectations.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation entails the division of a larger market into smaller, identifiable groups of consumers who exhibit shared characteristics. These characteristics may include demographic factors (such as age, gender, and income), psychographic traits (including lifestyle, values, and personality), behavioral patterns (like purchase frequency and brand loyalty), or geographic considerations (such as location and climate). By pinpointing specific market segments, businesses can direct tailored marketing messages and offers to particular customer groups, thereby enhancing the relevance and impact of their marketing initiatives.
Product Research
Product research is centered on comprehending customer perceptions regarding a product and its attributes. This domain encompasses the testing of various product concepts, the assessment of customer feedback, and the identification of features that consumers deem most valuable. Through methods such as product testing, prototype evaluations, and consumer trials, this research yields vital insights that inform product development, enhancement, and innovation.
Pricing Research
Pricing research focuses on establishing the most effective price point for a product or service. It seeks to understand the relationship between price and consumer purchasing behavior, including price sensitivity and willingness to pay. Utilizing techniques such as surveys and market analysis, this research provides essential data to guide pricing strategies.
Promotional Effectiveness
Research on promotional effectiveness assesses the impact of marketing campaigns, advertisements, and promotions on the intended audience. It analyzes the success of different promotional strategies in enhancing brand visibility, fostering customer engagement, and driving sales. By examining metrics such as reach, frequency, and conversion rates, organizations can determine which promotional efforts provide the highest return on investment (ROI).
Distribution Channels
The study of distribution channels aims to pinpoint the most efficient and effective methods for delivering products to consumers. It emphasizes the evaluation of supply chain management, retail approaches, and customer preferences regarding purchasing options (such as online versus in-store). Gaining insights into customer preferences for product delivery enables companies to refine their distribution systems and enhance customer satisfaction.
Market Trends and Competitor Analysis
Research in market trends and competitor analysis focuses on monitoring industry changes, shifts in consumer behavior, and new market opportunities. This field also investigates the strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning of competitors. By remaining aware of market trends and understanding competitive forces, businesses can make informed decisions to sustain a competitive edge.
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Research on customer satisfaction and loyalty evaluates the level of contentment customers experience with a company’s products or services. It identifies the elements that affect customer retention, repeat purchases, and brand allegiance. By collecting feedback through surveys, interviews, or online reviews, organizations can gain insights into the drivers of customer loyalty and enhance their service offerings to improve overall satisfaction.
Marketing Research Process
The Marketing Research Process adopts a systematic methodology that guarantees the collection, analysis, and application of data to effectively address particular marketing challenges or opportunities. This process is intricately linked to the Marketing Information System (MIS), as the insights derived from marketing research contribute to the MIS, thereby facilitating informed decision-making.
Problem Identification and Definition
The initial stage of the marketing research process involves identifying and defining the problem. This stage requires a precise articulation of the marketing issue or opportunity that the research aims to tackle. It also encompasses the establishment of research objectives and the formulation of critical questions that must be answered. A well-defined problem is essential for maintaining the research’s focus and relevance to the organization’s needs.
Research Design
During the research design phase, marketers select the most suitable research methodology. This may involve qualitative approaches, such as focus groups and interviews, to gain insights into attitudes and motivations, or quantitative methods, such as surveys and experiments, to collect numerical data and identify statistical relationships. Additionally, researchers determine the data collection techniques, sampling strategies, and tools to be employed in the study.
Data Collection
Following the establishment of the research design, the subsequent step is data collection. This phase entails the acquisition of primary data through fieldwork methods, including surveys, interviews, or focus groups. Secondary data, such as historical sales figures, market analyses, and competitor insights stored within the MIS, may also be utilized to enhance the primary research. The integration of both primary and secondary data provides a more thorough understanding of the marketing landscape.
Data Analysis
In the data analysis phase, the gathered data is processed, organized, and examined using various statistical methods and software applications. The primary objective of data analysis is to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations within the data.
Analysis and Insights
Following the data analysis, the subsequent stage involves deriving interpretations and insights. This phase focuses on converting the raw data into practical insights that align with the research goals. The principal findings are condensed and presented in a manner that is pertinent to business decision-making. These insights are typically conveyed through reports or presentations distributed to key stakeholders within the organization.
Reporting and Communication
During the reporting and communication phase, the research outcomes are assembled into comprehensive reports, executive summaries, or dashboards. These documents are then disseminated to pertinent stakeholders in the organization, including marketing managers, executives, and product development teams. The objective is to convey the findings in a clear and actionable manner to facilitate informed decision-making.
Execution and Evaluation
The concluding phase of the research process encompasses execution and evaluation. In this stage, the insights obtained from the research are implemented. Adjustments to marketing strategies, product designs, or promotional initiatives are made based on the research findings. Additionally, follow-up research may be conducted to assess the effectiveness of these modifications and to ascertain whether the initial objectives have been achieved.
Conclusion
A Marketing Information System (MIS) serves as an essential resource for organizations aiming to make informed, data-driven choices. It facilitates the collection, organization, and analysis of critical information regarding customers, competitors, and market dynamics, thereby empowering companies to develop effective marketing strategies. By synthesizing data from diverse sources, including internal records, marketing intelligence, and research, an Marketing Information System enhances decision-making processes and improves customer satisfaction. This system enables businesses to maintain a competitive edge by delivering timely insights that assist in adapting to market fluctuations. In summary, an Marketing Information System is indispensable for refining marketing initiatives and securing long-term business success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a Marketing Information System (MIS)?
A Marketing Information System (MIS) is a structured framework that systematically gathers, evaluates, and archives marketing-related data, enabling organizations to make well-informed decisions and develop successful marketing strategies.
Why is an Marketing Information System (MIS) important for businesses?
An MIS is crucial for organizations as it facilitates the collection of essential insights regarding the market landscape, customer behavior, and competitive dynamics, thereby enhancing decision-making processes and optimizing marketing effectiveness.
What are the main components of an MIS?
The primary elements of an MIS consist of internal data records, marketing intelligence, marketing research, and decision support systems.

