Marketing is the systematic approach to identifying, comprehending, and fulfilling the needs and desires of customers. This process entails the creation, communication, and delivery of value to consumers while simultaneously achieving the objectives of the organization. At its essence, marketing is centered on grasping customer behavior and preferences, designing products or services that cater to these needs, and facilitating exchanges that provide reciprocal value. It includes various components such as market research, product development, pricing strategies, promotional efforts, and distribution channels, all of which collaborate to cultivate customer relationships and enhance loyalty.
Marketing Management refers to the strategic planning, execution, and oversight of marketing initiatives aimed at attaining specific business goals. This involves the analysis of market trends, insights into consumer behavior, and the formulation of comprehensive marketing strategies that are in harmony with organizational objectives. Effective marketing management guarantees the optimal use of resources, the successful execution of campaigns, and the prioritization of customer satisfaction.
Table of Contents
Meaning of Marketing
Marketing encompasses the systematic approach through which organizations discern customer requirements, create products or services tailored to fulfill those requirements, and devise strategies for effective communication and delivery. It embodies both artistic and scientific elements, necessitating creativity, analytical capabilities, and strategic foresight.
Essential elements of marketing consist of:
- Customer Needs, Wants, and Demands: Gaining insight into customer preferences and aligning them with their financial capacity.
- Value and Customer Satisfaction: Developing products or services that deliver value and guarantee customer contentment.
- Exchanges and Transactions: Enabling the transfer of goods or services in return for monetary or alternative forms of value.
- Markets: The collective group of current and prospective purchasers for a specific product or service.
Evolution of Marketing Philosophies (Marketing Concepts)
The progression of marketing philosophies illustrates the evolving priorities and strategies that organizations have embraced over time to address customer requirements and fulfill their objectives. These philosophies, referred to as marketing concepts, have undergone several developmental phases:
The Production Concept
The production concept represents one of the foundational marketing philosophies, concentrating on production efficiency and extensive distribution. It was based on the premise that consumers would prefer products that are readily available and economically priced. This approach was particularly dominant during the industrial revolution, a period characterized by demand often surpassing supply. Consequently, businesses focused on mass production and cost minimization, largely neglecting customer preferences.
The Product Concept
The product concept arose from the belief that consumers would choose products that deliver superior quality, performance, and features. Organizations that embraced this philosophy placed significant emphasis on product innovation and enhancement. However, this focus sometimes caused companies to disregard customer needs and preferences, leading to the development of products that did not align with market demand.
The Selling Concept
As competition intensified and supply outstripped demand, businesses shifted their focus towards aggressive selling and promotional strategies. The selling concept posits that consumers will not purchase sufficient quantities of a product unless it is actively marketed and sold. This approach is particularly prevalent for unsought goods, such as insurance, where consumers may not initially recognize a need. However, it frequently neglects the importance of customer satisfaction and the cultivation of long-term relationships.
The Marketing Concept
The marketing concept represents a pivotal transformation in business philosophy, prioritizing the customer as the focal point of all activities. It underscores the importance of comprehending customer needs and providing superior value compared to competitors. The primary aim is to foster and sustain long-term relationships with customers by ensuring that products and services align with their preferences. This customer-oriented strategy gained prominence in the mid-20th century and continues to serve as a cornerstone of contemporary marketing practices.
The Societal Marketing Concept
In response to increasing societal and environmental issues, the societal marketing concept emerged. This philosophy builds upon the marketing concept by highlighting the importance of not only satisfying customer needs but also promoting the welfare of society and the environment. Organizations that embrace this approach seek to achieve a balance between profitability and ethical conduct, sustainability, and social accountability.
The Holistic Marketing Concept
The holistic marketing concept perceives marketing as a cohesive strategy, where all facets of the business are interrelated. It includes relationship marketing, internal marketing, integrated marketing, and socially responsible marketing. This philosophy acknowledges that effective marketing necessitates alignment within the organization and with external stakeholders to deliver consistent and meaningful value to customers.
Basic Principles of the Marketing Concept
The marketing concept is fundamentally centered on the customer, emphasizing the importance of comprehending and addressing customer needs more effectively than competitors. The key principles include:
Customer Orientation: The foremost objective is to identify and satisfy the needs and desires of target customers. Organizations strive to provide exceptional value that meets or surpasses customer expectations.
Integrated Marketing: All departments and functions within the organization must collaborate to support the marketing strategy, ensuring a cohesive customer experience.
Profitability Through Customer Satisfaction: This concept highlights the significance of long-term profitability achieved through fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty, rather than merely concentrating on immediate sales.
Market Research: Gaining insights into consumer behavior, market dynamics, and competitive landscapes is crucial for developing and offering products or services that resonate with customer preferences.
Value Creation: The organization should focus on creating and delivering value that is significant to customers, thereby distinguishing itself from competitors.
Basic Principles of the Holistic Marketing Framework
The holistic marketing framework adopts a comprehensive and integrated perspective on marketing, ensuring that all facets of the organization collaborate effectively to generate value. Its fundamental tenets include:
Relationship Marketing: Establishing enduring, mutually advantageous relationships with customers, employees, suppliers, and other stakeholders is paramount. This approach prioritizes customer retention, loyalty, and trust.
Integrated Marketing: All components of the marketing mix (product, price, place, promotion) and organizational processes must function in unison to convey a consistent and coherent message to customers.
Internal Marketing: Employees are regarded as internal customers. It is essential to ensure they are motivated, well-trained, and aligned with the organization’s objectives to provide exceptional customer experiences.
Social Responsibility Marketing: Organizations must take into account the wider implications of their activities on society and the environment. This involves adopting ethical practices, promoting sustainability, and making positive contributions to societal welfare.
Performance Marketing: The effectiveness of marketing strategies is assessed based on their influence on organizational objectives, such as profitability, market share, and brand equity, thereby ensuring measurable success.
While both concepts focus on customer satisfaction and value creation, the holistic marketing framework broadens its perspective to encompass wider societal and organizational alignment, ensuring that all stakeholders benefit from marketing initiatives.
Marketing Management
Marketing management encompasses the systematic planning and organization of activities aimed at promoting and selling products or services in a manner that satisfies customer requirements while simultaneously fulfilling business objectives. This discipline necessitates a comprehensive understanding of market opportunities, the formulation of strategic initiatives, and the implementation of plans designed to attract and retain customers. Ultimately, marketing management serves to bridge the gap between a business’s offerings and customer desires, emphasizing the delivery of value and the maintenance of profitability.

Tasks of Marketing Management
Marketing management entails several fundamental responsibilities that contribute to a business’s success in the marketplace.
Market Research and Analysis
The initial responsibility involves the collection of data regarding the market landscape. This process includes gaining insights into customer needs, preferences, and behaviors, as well as conducting analyses of competitors and prevailing market trends. Such information is crucial for enabling businesses to make well-informed decisions.
Establishing Marketing Objectives
Subsequently, businesses must define specific objectives, such as enhancing market share, fostering customer loyalty, or introducing new products. These objectives serve as a framework for guiding the organization’s marketing initiatives.
Formulating Marketing Strategies
Another critical aspect of marketing management is the development of strategies aimed at reaching the appropriate customer segments. This process involves market segmentation, identifying the target audience, and positioning the product to fulfill their requirements. Additionally, it includes the formulation of the marketing mix—comprising product, price, place, and promotion—to ensure alignment with these strategies.
Product Development and Management
Organizations must innovate new products or refine existing ones in response to customer demand. Effectively managing the product throughout its lifecycle is essential for maximizing profitability.
Pricing Strategies
Determining an appropriate pricing strategy is vital. Prices should reflect the perceived value of the product to customers, remain competitive within the market, and contribute to the business’s profitability.
Promotional Activities
Promotional efforts, including advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and digital marketing, are essential for conveying the product’s value to consumers and motivating purchase behavior.
Distribution and Logistics
The process of delivering products to customers is of paramount importance. Effective marketing management entails overseeing distribution channels to guarantee that products are delivered to customers efficiently and promptly.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Establishing robust relationships with customers is vital. This involves ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty to the brand through exceptional service and ongoing engagement over time.
Marketing in the Contemporary World
The landscape of marketing has experienced profound changes in recent years, driven by technological advancements, globalization, and shifting consumer behaviors. The following sections outline the essential elements of modern marketing.
Digital Marketing

The advent of the internet and social media has transformed the way companies engage with their customers. Digital marketing strategies, including search engine optimization (SEO), social media advertising, email campaigns, and content development, have become indispensable. These strategies enable businesses to effectively connect with their target audiences and offer personalized, immediate interactions that align with customer expectations.
Customer-Centric Focus
Today’s consumers are highly informed and have a plethora of choices, making a customer-centric approach essential. Companies prioritize understanding the needs, preferences, and behaviors of their customers to provide outstanding experiences. Fostering loyalty and trust through tailored interactions and addressing specific challenges has become fundamental to modern marketing tactics.
Emphasis on Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Contemporary consumers increasingly prefer businesses that exhibit social and environmental responsibility. Marketing strategies now highlight sustainable practices, environmentally friendly products, and support for social initiatives. Operating ethically not only fulfills customer expectations but also bolsters brand reputation and fosters loyalty.
Technological Innovation
The integration of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), virtual reality (VR), and blockchain has reshaped how businesses design and implement marketing campaigns. These technologies facilitate the creation of innovative and engaging experiences that distinguish brands in competitive environments. Maintaining adaptability and a forward-looking mindset is crucial for businesses to stay relevant.
Global Presence and Cultural Awareness
Globalization has broadened the horizons for businesses, allowing them to operate across various markets. However, this expansion necessitates a deep understanding of cultural nuances and sensitivities to effectively engage diverse audiences.
Data-Driven Marketing
In today’s marketing landscape, data and analytics are essential components. Organizations leverage data to gain insights into customer behavior, forecast trends, and tailor their marketing strategies. By utilizing data-driven insights, companies can refine their campaigns, enhance resource distribution, and attain superior results.
Real-Time Engagement
Modern consumers anticipate prompt responses and resolutions from businesses. The expectation for real-time engagement via social media, chatbots, and live support has become commonplace. Swift and efficient communication fosters stronger relationships and boosts customer satisfaction.
Marketing Challenges of the 21st Century
The 21st century has ushered in profound transformations within the business environment, presenting marketers with a range of challenges as they adapt to this evolving landscape. The following sections outline the primary challenges faced by marketers today.
Rapid Technological Advancements
The swift evolution of technology has introduced both opportunities and obstacles. Marketers are required to consistently adjust to emerging platforms, tools, and trends, including artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and big data analytics. To remain competitive, ongoing education and investment in innovative solutions are essential.
Increased Competition
The forces of globalization and enhanced digital access have escalated competition across various sectors. Organizations now find themselves competing not only with local entities but also with international brands. Establishing product differentiation and fostering robust brand loyalty in an overcrowded market has become a formidable challenge.
Changing Consumer Behavior
Modern consumers are more knowledgeable, technologically adept, and discerning. They demand personalized, immediate interactions and exhibit a low tolerance for generic communications. Meeting these expectations and ensuring customer satisfaction necessitates a comprehensive understanding of consumer preferences and behaviors.
Data Privacy and Security
As businesses increasingly gather data to provide tailored experiences, concerns regarding data privacy and security have intensified. Stricter regulations, such as the GDPR and CCPA, compel marketers to manage customer data with care while adhering to legal standards. Balancing the need for personalization with privacy considerations remains an ongoing challenge.
Managing Multichannel Marketing
The rise of various digital channels, including social media, mobile applications, and e-commerce platforms, has complicated marketing efforts. Marketers must devise integrated strategies that span multiple platforms while ensuring consistent messaging and effectively engaging customers in each channel.
Sustainability and Ethical Marketing
Consumers are progressively prioritizing sustainability and ethical considerations in their purchasing decisions. Marketers are challenged to align their strategies with these values, promoting responsible practices while meeting consumer expectations for transparency and accountability.
Adapting to Globalization
The global marketplace presents significant opportunities alongside various challenges. Marketers are required to address cultural, legal, and linguistic differences when expanding into international markets. It is a complex endeavor to tailor marketing strategies to cater to the diverse needs of audiences while preserving a cohesive brand identity.
Increasing Customer Demands
In today’s digital landscape, consumers anticipate swift and seamless services, tailored experiences, and immediate feedback. To satisfy these elevated demands, organizations must implement efficient systems, adopt flexible processes, and prioritize a customer-centric approach.
Firms’ Responses to Marketing Challenges in the 21st Century
In order to navigate the myriad challenges presented by contemporary marketing, firms are implementing innovative strategies and practices. The following outlines the primary methods by which businesses are addressing these challenges:
Utilizing Advanced Technologies
Companies are investing in cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and big data analytics to improve decision-making, automate operations, and provide personalized customer experiences. For example, AI-driven chatbots offer immediate customer support, while data analytics tools assist in identifying trends and opportunities.
Establishing a Distinct Brand Identity
To differentiate themselves in a competitive landscape, firms concentrate on creating a unique and cohesive brand identity. They engage in storytelling, authentic marketing, and the delivery of outstanding customer experiences to cultivate brand loyalty and distinction.
Analyzing and Adapting to Consumer Behavior
Businesses leverage data-driven insights to comprehend shifting consumer preferences and behaviors. By employing customer segmentation and personalization techniques, firms develop targeted campaigns that resonate with specific demographics, effectively addressing their needs and expectations.
Prioritizing Data Privacy and Compliance
In response to privacy concerns, firms implement transparent data policies and adhere to regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. They invest in secure systems to safeguard customer information and foster trust by clearly communicating their data handling practices to consumers.
Adopting Multichannel Marketing Approaches
Firms are embracing omnichannel marketing strategies to ensure a seamless and consistent customer experience across both digital and physical platforms. The integration of channels such as social media, email, e-commerce, and in-store interactions enhances engagement and overall effectiveness.
Committing to Sustainability and Ethical Practices
Companies are integrating sustainable practices into their operations and marketing strategies. They promote environmentally friendly products, adopt green supply chains, and actively support social initiatives, ensuring transparent communication regarding their efforts.
Relationship Marketing
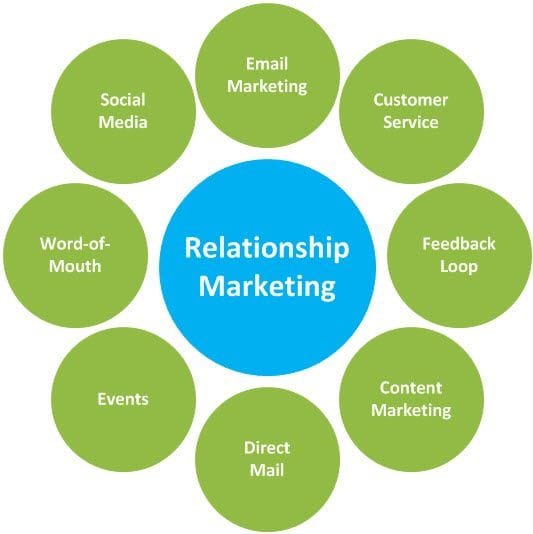
Relationship marketing is a strategic approach aimed at cultivating long-term connections with customers to improve loyalty and retention, rather than merely concentrating on individual transactions or immediate sales. The objective is to sustain continuous interactions with customers, thereby nurturing trust and engagement.
Concept of Relationship Marketing
The fundamental principle of relationship marketing is that by fostering a more profound relationship with customers, businesses can encourage repeat purchases, increase customer satisfaction, and establish a loyal clientele that is more inclined to recommend the business to others. This approach emphasizes creating enduring connections with customers through personalized experiences and a focus on their needs.
Relevance of Relationship Marketing
In the current competitive landscape, retaining existing customers is frequently more cost-effective than the ongoing pursuit of new ones. Relationship marketing is pertinent as it lowers customer acquisition costs and enables businesses to maintain a competitive advantage through elevated levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Practices of Relationship Marketing
Typical practices encompass personalizing communication, providing loyalty rewards or membership programs, employing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems to monitor customer preferences and behaviors, and delivering outstanding customer service. Additionally, implementing regular feedback mechanisms and tailored promotions are integral components of relationship marketing strategies.
Green Marketing
Green marketing pertains to the promotion of products, services, and business practices that prioritize environmental sustainability. It emphasizes offerings that have a minimal negative impact on the environment and integrates sustainability throughout all marketing facets, from production to packaging.
Concept of Green Marketing
The foundation of green marketing lies in the principle of environmental stewardship. Companies that adopt green marketing not only showcase the eco-friendly features of their products but also align their overall business strategies with sustainable and ethical practices. This may involve minimizing carbon emissions, utilizing recycled materials, or advocating for energy-efficient products.
Relevance of Green Marketing
With the increasing awareness of environmental issues among consumers, green marketing is becoming more significant. Consumers are more inclined to support brands that emphasize sustainability, and businesses that implement green marketing strategies can enhance their brand reputation, attract environmentally conscious customers, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Practices of Green Marketing
Green marketing practices include the use of recyclable or biodegradable packaging, promoting products that have a reduced environmental footprint (such as energy-efficient appliances), and ensuring that business operations minimize waste and emissions. Clear communication regarding sustainable practices is crucial, including eco-labeling and certifications.
Pyramid (C2C) Marketing
Pyramid marketing, commonly known as Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) marketing, entails individuals promoting and selling products or services to others, primarily within their personal networks. This model typically depends on individuals serving as brand ambassadors or sales representatives.
Concept of Pyramid (C2C) Marketing
The pyramid marketing framework emphasizes word-of-mouth sales and peer-to-peer engagement. It frequently includes incentivizing customers to recruit additional customers in return for rewards, such as commissions or bonuses. This model flourishes in network-oriented environments, where trust and personal relationships significantly influence sales.
Relevance of Pyramid (C2C) Marketing
C2C marketing holds significance in markets characterized by strong trust and social influence. This marketing approach capitalizes on personal networks and community ties to broaden the customer base. It is frequently employed in sectors such as direct sales, multi-level marketing (MLM), and various online platforms.
Practices of Pyramid (C2C) Marketing
Typical practices encompass the establishment of referral programs, providing rewards or commissions for new customer acquisitions or sales, and nurturing online communities where individuals can exchange experiences and testimonials. Effective C2C marketing often necessitates the development of a robust, loyal customer base willing to actively endorse products within their social networks.
Rural Marketing
Rural marketing pertains to the strategies and methodologies designed to promote products and services to consumers in rural or less urbanized regions. This marketing approach emphasizes understanding the specific needs and preferences of rural customers and adjusting marketing tactics accordingly.
Concept of Rural Marketing
Rural marketing acknowledges that rural consumers exhibit unique purchasing behaviors, income levels, and preferences that differ from those of urban consumers. It involves customizing products, pricing strategies, communication methods, and distribution channels to align with rural conditions. Additionally, rural marketing often addresses infrastructure challenges and aims to provide more affordable options.
Relevance of Rural Marketing
Given that a significant segment of the population resides in rural regions, rural marketing holds considerable importance, particularly in developing nations. Engaging with rural markets can enable businesses to broaden their outreach, enhance sales, and foster overall economic progress. Additionally, rural markets present unexplored avenues for growth.
Practices of Rural Marketing
Effective practices encompass the creation of affordable and durable products tailored to the needs of rural consumers, utilizing traditional media such as radio and local events for promotional activities, and establishing robust distribution channels (for instance, rural retail outlets and mobile vans). Emphasizing the cultivation of relationships with local communities is also essential. Furthermore, providing financing options and educating consumers about the advantages of products are critical components of rural marketing strategies.
Conclusion
Marketing and Marketing management play a crucial role in the success of a business, serving as a link between a company’s products and its intended audience. Marketing encompasses a wide range of activities aimed at recognizing and fulfilling customer needs while generating value. This includes making strategic choices regarding product development, pricing, promotion, and distribution, all with the goal of fostering enduring relationships with customers.
Conversely, marketing management pertains to the systematic approach of planning, implementing, and overseeing these marketing initiatives to achieve the objectives of the organization. This process involves examining market trends, comprehending consumer behavior, and employing various strategies to secure sustainable growth. Effective marketing management guarantees that the organization remains responsive to evolving market dynamics and competitive landscapes, all while prioritizing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is Marketing?
Marketing encompasses the activities involved in recognizing, predicting, and fulfilling the needs and wants of customers through various products, services, and communication methods.
2. What is Marketing Management?
Marketing management involves the strategic planning, execution, and oversight of marketing initiatives aimed at meeting organizational objectives, with an emphasis on providing value to customers in a proficient and effective manner.
3. What is the importance of marketing?
Marketing plays a crucial role in enabling businesses to comprehend customer requirements, generate awareness, and foster robust customer relationships, ultimately resulting in enhanced sales and increased brand loyalty.

