Leadership

Leadership is about guiding and inspiring a group of people to work towards a common goal. A leader helps set the direction, makes decisions, and motivates others to stay on track. A good leader builds trust, encourages teamwork, and helps solve problems when needed.
Table of Contents
Motivation

Motivation is what drives you to take action and work toward your goals. It can come from within, like the desire to succeed or enjoy something, or from outside, like rewards or praise. Motivation helps you stay focused and keep going, especially when things get tough.
Leadership: Concept, Importance and types
Leadership is the ability to guide, influence, and inspire others toward achieving common goals. A leader motivates people, provides direction, and helps a team work together effectively. Leadership is not just about authority it’s about encouraging others and setting an example through actions and decisions.
Importance of Leadership
The significance of Leadership are
Provides Direction
Leaders set clear goals and guide the team on how to achieve them, ensuring everyone is aligned and focused.
Motivates and Inspires
A good leader motivates the team, boosting their confidence and encouraging them to perform at their best.
Builds Teamwork
Leadership helps create a sense of unity and cooperation among team members, fostering collaboration and trust.
Facilitates Decision Making
Leaders make decisions when needed, ensuring that progress is not delayed and challenges are addressed effectively.
Drives Change
Strong leadership is essential for managing change in organizations, helping teams adapt to new situations and overcome obstacles.
Improves Performance
Effective leadership enhances the overall performance of a team or organization by keeping everyone focused and committed to their roles.
Types of Leadership
Autocratic Leadership
An autocratic leader makes all the decisions and expects the team to follow without questioning. This style works well in emergencies or when quick decisions are essential. However, it can sometimes limit creativity and reduce team involvement.
Democratic Leadership
Democratic leaders involve their team in decision-making and value everyone’s input. This style encourages creativity and collaboration and is most effective when team participation is critical to success.
Laissez-Faire Leadership
In laissez-faire leadership, the leader gives the team full freedom to make decisions and work independently. It works best for skilled and self-motivated teams but can lead to confusion if members lack direction or support.
Transformational Leadership
Transformational leaders inspire and motivate their team to achieve extraordinary goals. They focus on innovation, growth, and the personal development of team members, making them effective at driving change and realizing long-term visions.
Transactional Leadership
This style is based on a system of rewards and punishments. Transactional leaders set clear tasks and goals and reward the team for achieving them. It works well in structured environments with specific targets.
Charismatic Leadership
Charismatic leaders use their personality and charm to inspire their team. They build strong emotional connections, but this style may rely too much on the leader’s individual influence, which can pose challenges if the leader is absent.
Each leadership style has its strengths and weaknesses, and the effectiveness of a style depends on the situation and the team being led.
Management versus Leadership
Concept of Management
Management is about organizing resources like people, money, and time to achieve specific goals. Managers focus on planning, directing, and controlling tasks to ensure everything runs smoothly. Their goal is to maintain stability and consistency in daily operations.
Concept of Leadership
Leadership is about inspiring and motivating people to work toward a shared vision or goal. Leaders focus on building strong relationships, encouraging creativity, and driving change. They prioritize guiding people and helping them perform at their best.
Key Differences Between Management and Leadership
Focus and Goals
Management is about organizing tasks, systems, and resources to make sure work gets done smoothly. Managers focus on achieving specific goals and maintaining order. Leadership, on the other hand, is about inspiring people and guiding them toward a bigger vision or future goals.
Approach and Style
Managers follow rules, systems, and plans to ensure everything is structured and efficient. Leaders take a different approach by encouraging creativity, taking risks, and trying new ideas to bring about change. While managers control and organize, leaders inspire and motivate.
Authority vs. Influence
Managers use their position or authority to get things done. They rely on their role in the organization to direct others. Leaders, however, rely on influence and trust. They inspire people to follow them because they believe in their vision, not just because of their title.
Time Perspective
Management focuses on short-term goals and day-to-day tasks. It’s about solving immediate problems and staying on track. Leadership is focused on the future, guiding the team toward long-term success and growth.
Decision-Making
Managers make decisions using rules, data, and past experience to minimize risks. Leaders make decisions based on their vision and intuition, focusing on future opportunities and adapting to changes.
Emotional intelligence in leadership: Concept, importance and components
What is Emotional Intelligence in leadership?
Emotional intelligence (EI) in leadership means a leader’s ability to understand and control their own emotions, as well as understand and influence the emotions of others. It involves being aware of one’s feelings, managing them well, showing empathy, and building strong relationships with others. Leaders with high emotional intelligence can handle stress better, communicate more effectively, and motivate their team to do their best work.
Why Emotional Intelligence is important for leaders?
Building Strong Connections
Leaders with good EI build trust and strong relationships with their team, creating a positive atmosphere at work.
Better Communication
EI helps leaders understand the emotions behind what people are saying, leading to more effective and empathetic communication.
Improved Decision-Making
Emotionally intelligent leaders can manage their emotions, making it easier for them to make fair and thoughtful decisions.
Solving Problems
Leaders with EI can handle conflicts calmly and work to find solutions that satisfy everyone involved.
Boosting Team Spirit
A leader with EI can motivate their team, keeping everyone focused and helping them overcome challenges.
Adapting to Change
Emotionally intelligent leaders stay steady and positive during uncertain or difficult times, helping their team adapt as well.
Components of Emotional Intelligence in Leadership
Self-Awareness
Knowing and understanding your own emotions and how they affect your actions. Leaders who are self-aware can manage their feelings better and stay in control.
Self-Management
The ability to control your emotions, especially during stressful moments. Leaders with self-management stay calm and clear-headed.
Social Awareness
Being able to understand and empathize with others’ feelings. Leaders who are socially aware know what their team needs and can respond appropriately.
Relationship Management
Building and keeping good relationships with others. This involves clear communication, teamwork, and resolving issues effectively.
Motivation: Concept, types and techniques
What is Motivation?
Motivation is the inner drive or desire that pushes people to act and achieve their goals. It’s what makes individuals work harder, stay focused, and put effort into their tasks. In management, motivation plays a key role in inspiring employees to perform at their best and contribute to organizational success.
Types of Motivation
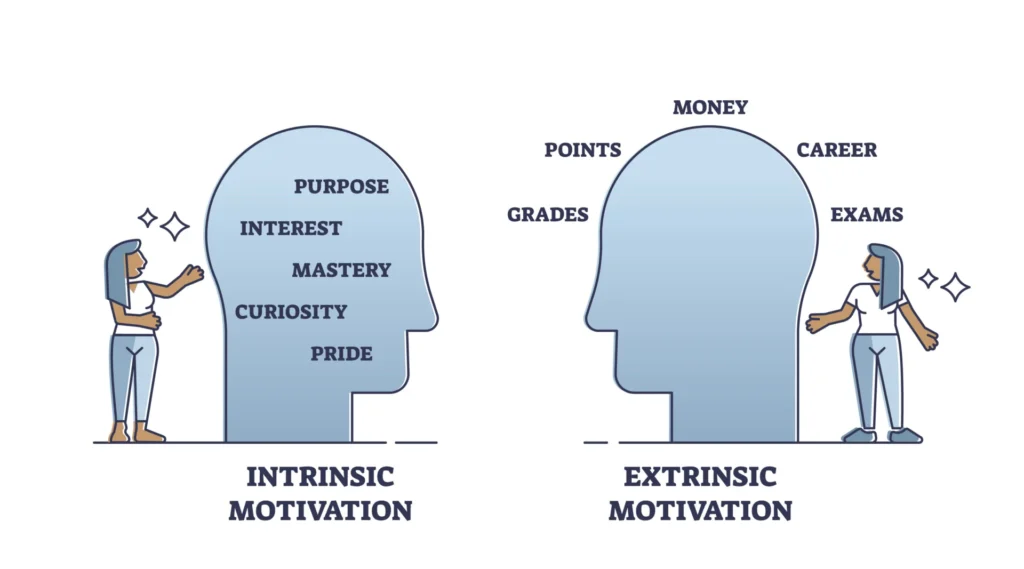
Intrinsic Motivation
This type of motivation comes from within a person. It’s driven by personal satisfaction, interest, or a sense of achievement. People motivated intrinsically enjoy what they do and feel rewarded by the activity itself. For example, an employee may work hard on a project because they find it exciting and want to learn more, not because of a reward.
Extrinsic Motivation
Extrinsic motivation is influenced by external factors like rewards, praise, or avoiding penalties. It drives people to take action to gain something tangible, such as a bonus, or to avoid consequences like criticism. For example, an employee may work overtime to earn extra pay or to meet a deadline and avoid complaints. While effective for short-term goals, it may not sustain long-term enthusiasm.
How to Motivate People
Set Clear Goals
When goals are clear and easy to understand, people know what they need to do and stay focused on achieving them.
Reward Efforts and Recognize Achievements
Providing rewards like bonuses, promotions, or simple praise motivates people to keep working hard. Recognizing efforts makes them feel valued.
Offer Opportunities to Grow
Employees feel motivated when they have a chance to develop their skills or advance in their careers. Training, learning opportunities, and promotions keep them engaged.
Create a Positive Work Environment
A supportive and friendly workplace encourages motivation. Open communication, teamwork, and mutual respect make employees feel valued and included.
Involve Employees in Decisions
When employees are part of the decision-making process, they feel more involved and committed to their work.
Provide Feedback
Giving regular feedback helps employees understand what they’re doing well and where they can improve. Positive feedback builds confidence, while constructive criticism helps them grow.
Motivation is essential for success. It drives people to work hard, achieve goals, and contribute positively. Understanding the difference between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation helps managers use the right techniques to inspire their teams. By setting clear goals, recognizing achievements, offering growth opportunities, and fostering a supportive environment, organizations can keep their employees motivated and achieve long-term success.
Theories of Motivation
Maslow’s Need Hierarchy Theory
Maslow’s theory says that people have five levels of needs, and they are motivated to fulfill these needs one step at a time:
Physiological Needs: These are basic needs like food, water, and shelter. Until these are met, people can’t focus on anything else.
Safety Needs: Once basic needs are met, people want to feel secure in their jobs, homes, and health.
Social Needs: Next, people seek relationships, friendships, and a sense of belonging.
Esteem Needs: After social needs, people want respect, recognition, and to feel accomplished.
Self-Actualization: At the top, people aim to reach their full potential and achieve personal growth.
According to Maslow, satisfying each level of need motivates people to move to the next level.
McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
This theory focuses on how managers view and motivate employees:
Theory X: Managers believe employees dislike work, avoid responsibility, and need constant supervision. To motivate them, managers use strict rules, control, and rewards or punishments.
Theory Y: Managers believe employees enjoy work, take responsibility, and are self-motivated. They focus on giving employees freedom, trust, and opportunities to grow.
McGregor suggests that Theory Y is more effective for creating a positive and productive work environment.
Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory
Herzberg’s theory explains what makes people satisfied or dissatisfied at work:
Hygiene Factors: These are basic things like salary, job security, work conditions, and company policies. If these are missing, employees become dissatisfied, but having them doesn’t necessarily make employees happy.
Motivators: These are factors that truly inspire people, like recognition, achievement, growth opportunities, and meaningful work. These make employees feel satisfied and motivated.
Herzberg’s theory shows that organizations need both hygiene factors and motivators to keep employees happy and productive.
These motivation theories highlight different ways to understand and inspire people. Maslow’s hierarchy explains the step-by-step nature of motivation, McGregor’s theory shows how a manager’s approach affects employees, and Herzberg’s theory focuses on creating satisfaction at work. By applying these ideas, organizations can better meet employees’ needs and improve overall performance.
Current issues in motivation
Keeping employees motivated is harder today due to changes in the workplace. Here are some common challenges and how to deal with them:
Stress and Burnout
Employees often feel overwhelmed with heavy workloads and constant pressure, which reduces motivation. Companies can help by promoting a healthy work-life balance, providing mental health support, and encouraging regular breaks.
Remote Work Difficulties
Working from home can make employees feel isolated and disconnected from their teams. To keep them motivated, businesses need to maintain good communication, build team spirit, and recognize achievements even in virtual settings.
Limited Career Growth
When employees don’t see opportunities to grow in their roles, they lose motivation. Offering training, mentoring, and clear career paths can help keep them engaged.
Lack of Recognition
When hard work isn’t acknowledged, employees feel unappreciated. Regular praise, rewards, and involving employees in decisions can make them feel valued and motivated.
Adapting to Technology
New tools and systems can feel overwhelming for some employees. Providing proper training and support can help them adapt and stay motivated.
Job Insecurity
Uncertain times, like economic changes or company restructuring, can make employees worry about losing their jobs. Clear communication and reassurance from management can help reduce fear and keep them focused.
Motivating employees today means understanding their challenges and supporting them. By addressing stress, recognizing efforts, offering growth opportunities, and fostering teamwork, organizations can create a positive and motivated workplace.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
What are the main challenges in motivating employees today?
Some key challenges include employee burnout and stress, difficulties with remote work, limited career growth opportunities, lack of recognition, generational differences, adapting to new technologies, and job insecurity.
How can companies address employee burnout and stress?
Organizations can reduce burnout by promoting a healthy work-life balance, offering mental health support, encouraging regular breaks, and creating manageable workloads.
What role does recognition play in employee motivation?
Recognition makes employees feel valued and appreciated for their hard work. Regular praise, rewards, and involving employees in decision-making boost motivation and engagement in the workplace.
Related Articles

