The strategic and methodical approach to managing an organization’s most valuable assets its people is known as Human Resources Management, or HRM. It entails hiring, choosing, educating, growing, and keeping staff members while also making sure they are happy and that their objectives line up with those of the company. In order to build a productive workplace, promote employee happiness, and propel organizational success, human resource management is essential.
Table of Contents
The Concept of Human Resources Management (HRM)
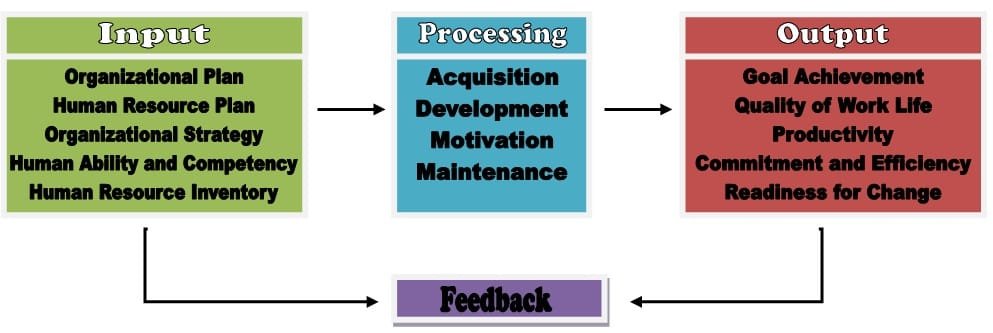
The art of procuring, developing and maintaining competent workforce to achieve the goals of an organization in an effective and efficient manner. Human Resources Management is the function performed in organization that facilitates the most effective use of people to achieve organizational and individual goals.
According to DeCenzo and Robbins “Human resource management is comprised of the acquisition, development, motivation and maintenance function of human resource.”
Nature of Human Resources Management
- Human Focus
- Management Function
- Pervasive Function
- Continuous Function
- Dynamic
- System
- Mutuality Oriented
Importance/Objectives of Human Resources Management
• Effective Utilization of Resources
• Organizational Structure
• Development of Human Resource
• Respect for Human Beings
• Goal Harmony
• Employee Satisfaction
• Organizational Productivity
Functions/Components of Human Resources Management
Acquisition
| Human Resource Planning | Job Analysis | Recruitment | Selection |
| Process of pre- determining future man power needs. | Process by which the facts with respect to each job are systematically discovered. | Searching for and obtaining qualified job candidates. | Choosing the most suitable person for vacant post. |
Development
| Employee Training | Management Development | Career Development |
| An effort by an organization to facilitate employees learning. | Process of training and growth by which individuals gain and apply knowledge and skill. | Tracking career paths of employees. |
Utilization
| Motivation | Performance Appraisal | Compensation Management |
| Willingness to expand energy to achieve a goal. | Evaluation of individuals with respect to their performance on the job. | Distributing fair reward based on ability & legal regulation. |
Maintenance
| Labor Relation | Employee Discipline | Grievance Handling | Employee Welfare |
| Relationship between workers, employers and government. | Condition in the organization where employees conduct themselves in accordance with organization’s rules. | Handling of employee’s dissatisfaction or feeling of injustice. | Various activities such as recreation, sports, proper air safety. |
Human Resources Management (HRM) System
Changing Role of HR Manager
Flatter Organization
It is reducing levels of hierarchy mean that more people report to one manager. Therefore, employee will have to work on their own will with less interference from the manager.
Employee Empowerment
Knowledge workers need to be provided with greater autonomy through information sharing and provision of control over factors that affects performance.
Team Work
Employee contribute to the organization more as a member of team. Workers should be managed as a team and not as an individual.
Ethical Management
It pose fundamental questions about fairness, justice, truthfulness and social responsibility. HR manager ought to act relative to a given human resource issues.
Challenges of Human Resources Management
- Globalization
- Technological Advances
- Nature of Work: shift of jobs from manufacturing to service industries
- Work Force Diversity
- Less Attached Employees: part-time, temporary employees
- New HRM Concern: management of work team, addressing the interest of weaker section of society (women, minority groups)
- Change Management
- Learning Organization: creating, acquiring and transferring knowledge.
Essential Skills for HR Managers
- Effective Communication Skill
- Change Management Skill
- Leadership Skill
- Technological Skill
- Decision Making Skill
- Motivation Skill
- Multitasking Skill
- HR Knowledge and Expertise Skill
Dimensions of HRM
HR Practice and Performance
If the human resources are managed properly, they can contribute to the success for the company. The effective performance of human resource is possible through the implementation of sound HRM practices.
Organization can decide that the most performing employees within their department will be bought for a house or a car. In such a scenario, most of the employees will tend to work hard in order to get the prize and this will positively influence the performance of the company.
Re-engineering of the Organization
Reengineering involves the radical redesign of core business processes to achieve dramatic improvements in productivity. Re-engineering identifies, analyzes, and re-designs an organization’s core business processes with the aim of achieving improvements in critical performance measures, such as cost, quality, service, and speed.
For example, Organization decides to reshuffle all the employees to improve the level of performance that can bring about growth.
Leadership
Good leadership in an organization can bring about good performance among the employees but poor leadership which undermines the employees will automatically discourage them and hinder the level of their performance.
For example, the managers of an organization select the best performing employees and groom them for the future top job and even put them to test.
Workplace Learning
Workplace learning usually refers to the processes of learning through and for engaging in paid employment: on-the-job learning or learning through work.
Workplace learning helps people build the skills and knowledge they need to do their jobs.
HRM as a Shared Function
HRM as a shared function refers to a model in which HR responsibilities and tasks are distributed and shared among various stakeholders within an organization, rather than being centralized within a dedicated HR department. Basically, line managers are encouraged to take part in HRM functions and deliver the responsibilities. HR managers are encouraged to participate in formulation of business strategies in the organizations.
When HR and line management work together, it’s easier for HR to investigate workplace issues. Human resource professional will plan and establish systems which will allow the managers to make best use of their subordinates. HR professional will advise and train managers on how to utilize their subordinates in order to achieve the department objectives. Dealing with disciplinary and performances issue is another conflict between HR officer and department head. Most HOD, feels uncomfortable dealing with discipline matters they rather pass to HR Manager.
Structure of HR Department
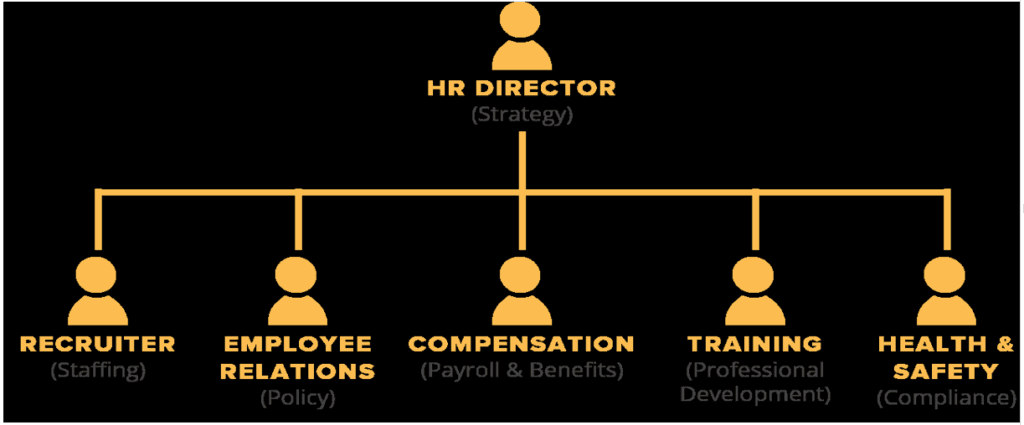
Recruiter: HR planning, Recruitment, selection, placement
Employee Relation: Dispute resolution, grievance handling, contract negotiation, labor laws etc.
Compensation: Job evaluation, attendance checking, salary policy administration, bonus managing, incentive payment etc.
Training: Orientation, Training appraisal, promotion policy
Health and Safety: job safety, maintaining healthy work environment, stress, etc.
Internal Context of HRM
The internal context essentially refers to the inner context, that is, the organizational environment within which HR management takes place. It is located within the organization. It is controllable by HRM. It provides strength and weakness to HRM.
Forces of Internal Environment
HRM Scope: Organizational goals, Policies, Strategies, Organizational Structure, Resources, Organizational Culture.
Organizational Activities: Production, Marketing, Finance etc.
Stakeholders: Labor union, Employees etc.
External Context of HRM
It consists of conditions and forces external to HRM. It can not be controlled by HRM. It influences the performance and outcome of HRM by providing opportunity and threat. Forces are-Physical forces, Political and legal forces, Economic forces, Socio cultural forces and Technological forces (PEST).
Physical Forces: Topography, climate
Political forces: Political system, institutions and philosophy
Legal forces: Law, rules, regulations, court cases
Economic forces: Globalization, demography, economic health
Socio-Cultural forces: Social norms, life style, religion, traditions
Technological forces: Level of technology, technological change
HRM in Nepal
HRM in Nepal is mainly concerned with utilizing human energies. It is least concerned with developing human competencies and potential of employees. People are not considered as important assets of the organization. Managers are discipline, control and direction oriented. Nepal has poor tradition of HR planning. Most of government agencies suffer from overstaffing. Job analysis has remained an underutilized tool. Public enterprises lack proper job description.
For all open competition-oriented posts, recruitment is done by the public service commission. Training needs are not properly assessed. Organizations use a mix of on-the-job and off-the-job training methods. Almost all trainings are underfunded and mismanaged. Motivation has remained a neglected aspect. Performance evaluation lacks transparency. It is promotion oriented. Compensation practices are largely concerned with pay and benefit.
Conclusion
The ability to fully utilize the potential of employees is made possible by Human Resources Management, or HRM. HRM guarantees that the company can prosper over the long term, adapt to changing conditions, and cultivate employee happiness by coordinating human resources with strategic objectives.
The fundamental tenets of Human Resources Management (HRM) are human focus, managerial efficiency, and mutuality help to close the gap between employee goals and organizational objectives. Its significance at every organizational level is highlighted by its ubiquitous and ongoing nature. Additionally, HRM’s dynamic and methodical approach allows it to tackle difficult issues like technological advancements and globalization.
HRM is essentially the foundation of organizational growth, making sure that the organization and its employees prosper together.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
HRM is the process of effectively managing people in an organization to meet its objectives while maintaining employee growth and satisfaction.
What are the main functions of HRM?
HRM is the process of effectively managing people in an organization to meet its objectives while maintaining employee growth and satisfaction.
Why is HRM important?
HRM makes sure that a company has the right people, processes, and abilities to accomplish its goals while preserving employee happiness and engagement.

