Consumer behavior encompasses the analysis of how individuals, groups, or households make choices regarding the selection, acquisition, utilization, and disposal of goods or services to fulfill their needs and wants. This field investigates the psychological, social, cultural, and personal elements that impact these decision-making processes. Gaining insights into consumer behavior is crucial for businesses to develop effective marketing strategies and provide products that resonate with customer preferences.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Consumer Behavior
In the current fast-paced and competitive marketplace, it is crucial for businesses to comprehend consumer behavior in order to effectively customize their products, services, and marketing approaches. By examining the factors that influence consumer motivations, their information-seeking behaviors, and the elements that shape their preferences, companies can anticipate purchasing trends, improve customer satisfaction, and foster enduring loyalty.
Furthermore, the exploration of consumer behavior not only contributes to the success of businesses but also provides insights into wider societal and economic patterns, establishing it as an essential area of study for marketers, economists, and policymakers.
Consumer Buying Process
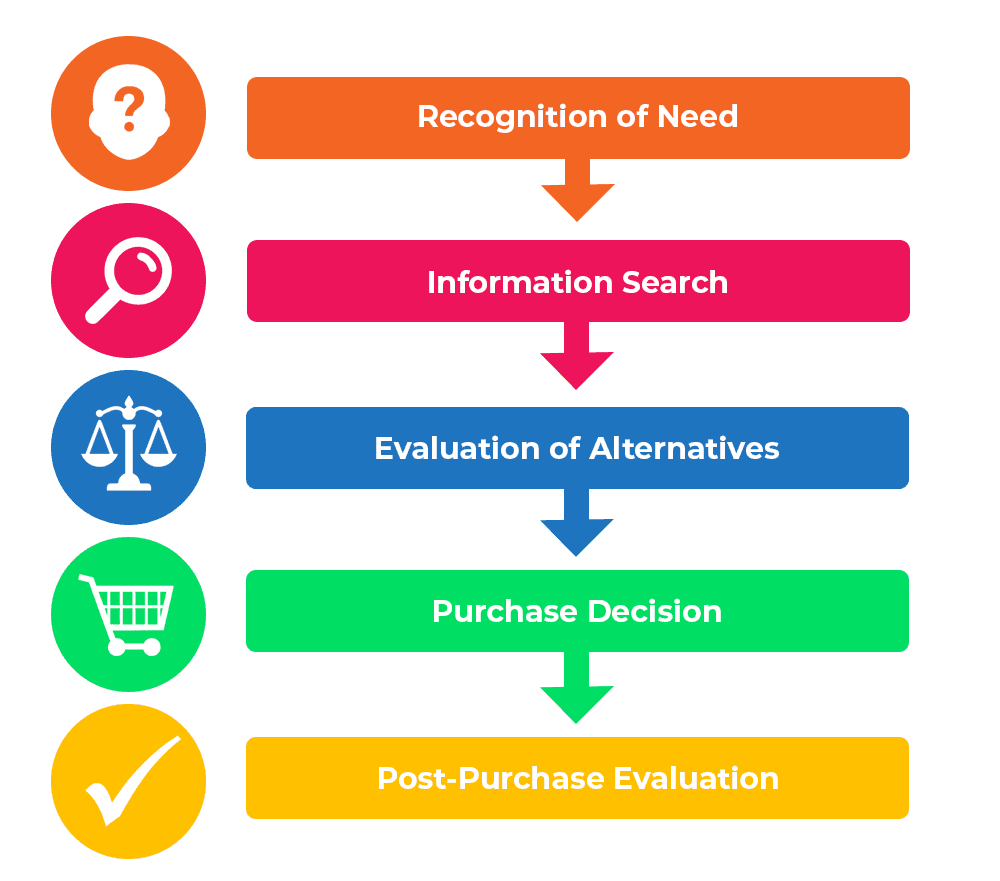
The consumer purchasing process consists of a structured sequence of stages that individuals undertake when contemplating a purchase. It commences with the identification of a problem, wherein the consumer acknowledges a need or want, such as the necessity to replace an item or to find a resolution to a particular issue. Following this recognition, the subsequent phase involves the search for information, during which consumers collect data regarding possible solutions. This information-gathering can be conducted internally, drawing on past experiences, or externally, through resources such as advertisements, online reviews, or personal recommendations.
The consumer purchasing process is a systematic method that individuals utilize when deciding to make a purchase. This process encompasses several distinct stages:
Problem Identification
This initial phase involves the consumer recognizing a need or issue that necessitates a solution. For instance, one may become aware that their smartphone is no longer current or that their food supplies are dwindling. This acknowledgment marks the beginning of the purchasing process.
Information Gathering
Following the identification of a need, the consumer embarks on a quest for information to uncover possible solutions. This may involve reflecting on personal experiences, consulting friends or family, perusing online reviews, or examining advertisements. The extent of this search is influenced by the complexity and significance of the intended purchase.
Comparison of Options
During this phase, consumers assess various products or services against criteria such as cost, quality, features, and brand reputation. For example, an individual seeking a laptop may evaluate several brands, specifications, and price points before making a decision.
Decision to Purchase
Upon completing the evaluation of alternatives, the consumer chooses the product or service that most effectively fulfills their needs and proceeds with the purchase. Influencing factors may include promotions, ease of access, and trust in the brand.
Post-Purchase Evaluation
Subsequent to the purchase, the consumer reflects on their satisfaction with the product or service. Positive experiences can lead to repeat purchases and brand loyalty, whereas dissatisfaction may result in returns, complaints, or a shift to competing brands.
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
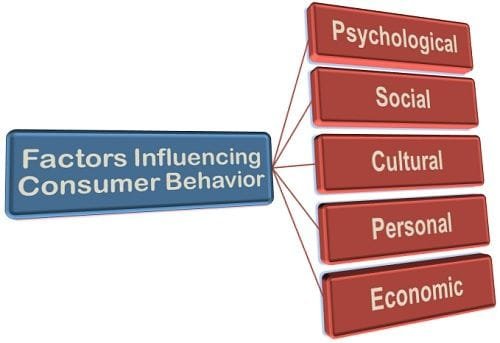
Consumer behavior is shaped by a multitude of factors that influence their needs, preferences, and decision-making processes. These factors encompass cultural, social, personal, psychological, and situational influences.
Cultural Influences
Culture plays a crucial role in shaping consumer behavior by establishing values, beliefs, and norms. Within a broader culture, subcultures, including ethnic and religious groups, often display unique preferences. Additionally, social class, which is influenced by income, education, and occupation, affects purchasing habits, with individuals from higher social classes typically gravitating towards premium products.
Social Influences
The dynamics of social interactions and relationships are essential in guiding consumer choices. Reference groups, such as friends, colleagues, or social media influencers, can sway preferences through their recommendations or endorsements. Family also serves as a significant influence, particularly in joint purchasing decisions. Furthermore, an individual’s roles and societal standing may dictate their buying behavior to conform to social norms.
Personal Influences
Individual characteristics, including age, occupation, and lifestyle, significantly impact consumer choices. For instance, younger consumers may prioritize trends in fashion and technology, while older consumers might emphasize health and comfort. Economic factors, such as income and financial security, also play a critical role in determining purchasing power, influencing whether consumers choose luxury items or more economical options.
Psychological Influences
Internal factors such as motivation, perception, and attitudes are pivotal in shaping consumer decision-making. Motivation drives consumers to fulfill needs, ranging from basic necessities to higher aspirations like social status. Perception influences how consumers interpret product information, while past experiences and brand beliefs inform future purchasing behavior.
Situational and Environmental Influences
External factors, including economic conditions, technological developments, and specific situational contexts, also affect consumer behavior. For example, changes in economic trends can alter consumer spending habits.
Consumer Movement and Consumer Protection
The principles of consumer movement and consumer protection are centered on guaranteeing fair treatment for consumers and safeguarding their rights within the marketplace. The following is a comprehensive overview structured under key headings:
Consumer Movement

The consumer movement represents a social and economic initiative designed to empower individuals to advocate for fair treatment, ethical business conduct, and corporate accountability. It arose in response to various unfair trade practices, including price manipulation, misleading advertising, and the distribution of inferior products.
Objectives of the Consumer Movement
- Awareness: Inform consumers about their rights and responsibilities to facilitate informed decision-making.
- Advocacy: Advocate for the implementation of robust laws and regulations that protect consumer interests.
- Equity: Promote fair trade practices and ensure equitable treatment for all consumers.
- Sustainability: Encourage environmentally responsible and ethical consumption practices.
Impact of the Consumer Movement
The consumer movement has resulted in the creation of regulatory frameworks, enhanced business transparency, and heightened consumer awareness. It empowers individuals to demand superior services, higher-quality products, and greater accountability from businesses.
Consumer Protection
Consumer protection encompasses the legal and institutional frameworks established to shield consumers from exploitation and to uphold their rights. It ensures that businesses engage in fair practices while providing consumers with the necessary information and safeguards.
Essential Components of Consumer Protection
Legal Rights for Consumers
Consumers possess several essential rights, including:
- Right to Safety: Safeguards against products that may pose risks to health or life.
- Right to Information: The entitlement to accurate information regarding goods and services.
- Right to Choice: The ability to select products freely without undue pressure.
- Right to Redress: Access to processes for resolving complaints and seeking compensation.
- Right to Education: Knowledge about consumer rights and responsibilities.
Consumer Protection Legislation
Governments enact laws aimed at protecting consumers from fraudulent activities, misleading advertising, and substandard products. Notable examples include regulations on product liability, anti-fraud statutes, and fair trading laws.
Regulatory Bodies
Dedicated agencies or councils are established to enforce consumer protection legislation. They handle disputes, monitor market practices, and ensure adherence to legal requirements.
Consumer Advocacy Groups
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and consumer rights advocates actively promote awareness, campaign for enhanced protections, and support consumers in legal matters.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
An increasing number of businesses are embracing ethical practices, such as truthful advertising, transparent communication, and environmentally responsible operations, in alignment with the principles of consumer protection.
Conclusion
Consumer behavior represents a multifaceted and evolving domain that illustrates the purchasing decisions made by individuals, groups, or organizations. For businesses, comprehending consumer behavior is crucial for effectively customizing their products, services, and marketing approaches. By examining the various factors that impact decision-making including cultural, social, personal, and psychological influences companies can anticipate buying trends, enhance customer satisfaction, and foster brand loyalty.
In a competitive landscape, it is vital for businesses to align their offerings with the needs and preferences of consumers to achieve success. Analyzing consumer behavior not only supports the prosperity of businesses but also guarantees that consumers derive value and satisfaction from their purchases, thereby establishing a mutually advantageous relationship.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Consumer Behavior?
Consumer behavior refers to the examination of the processes by which individuals, groups, or organizations determine their choices regarding the selection, acquisition, utilization, and disposal of goods and services.
Why is Consumer Behavior important for businesses?
Grasping consumer behavior enables businesses to customize their offerings, services, and marketing approaches to align with customer needs and preferences, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and fostering loyalty.
What factors influence consumer behavior?
Consumer behavior is shaped by a variety of factors, including cultural, social, personal, psychological, and situational influences.

