Buyer behavior encompasses the actions, choices, and processes that individuals or organizations engage in when they select, acquire, utilize, or dispose of products or services. This concept includes the motivations, preferences, and various factors that affect the purchasing decisions of both consumers and businesses. Gaining insight into buyer behavior is essential for companies to develop effective marketing strategies, fulfill customer requirements, and sustain a competitive advantage.
Table of Contents
Buyer Behavior
Buyer behavior encompasses the actions and decision-making processes undertaken by individuals or groups in the acquisition of products or services. This concept includes the motivations driving their purchasing decisions, the various factors that sway their choices, and the phases they experience before, during, and after the transaction. Gaining insight into buyer behavior is essential for businesses, as it enables them to develop effective marketing strategies, refine product offerings, and improve customer satisfaction.
Key Factors Influencing Buyer Behavior
Psychological Elements
These encompass a consumer’s perceptions, motivations, beliefs, and attitudes regarding a product or service. For instance, individual preferences or emotional responses may lead consumers to favor one brand over another.
Social Elements
Social factors such as family, friends, colleagues, and social media significantly impact purchasing decisions. Individuals are frequently swayed by the views and actions of those in their social circles.
Cultural Elements
Cultural background, subcultures, and social class contribute to the formation of buying behavior. Individuals from diverse cultural contexts may possess distinct preferences and values that influence their purchasing choices.
Economic Elements
A consumer’s income, financial circumstances, and broader economic conditions (such as inflation or recession) affect their purchasing power and decision-making processes. For example, an individual may refrain from making luxury purchases during a period of economic decline.
Personal Elements
These consist of factors such as age, profession, lifestyle, and life stage, which can shape a consumer’s preferences. For instance, younger individuals may lean towards fashionable items, while older consumers may focus on quality and longevity.
Organizational Buyer Behavior
Organizational buyer behavior pertains to the process through which businesses, institutions, and governmental bodies arrive at purchasing decisions. In contrast to consumer buying behavior, which emphasizes individual preferences, organizational buying is characterized by a more structured approach, often involving several decision-makers. This process is generally driven by defined business requirements and goals. Organizational buyers prioritize aspects such as cost efficiency, operational effectiveness, product quality, supplier dependability, and long-term value, rather than emotional or personal factors.
Buying Process in Organizational Buyer Behavior
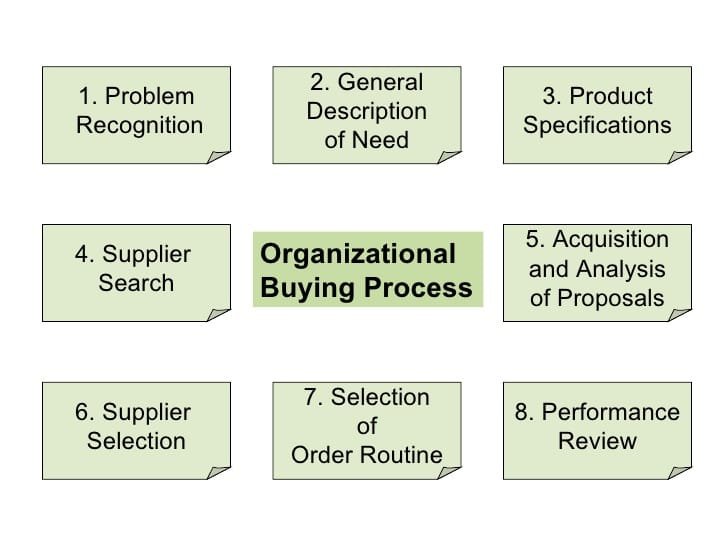
The purchasing process that organizations undergo to make buying decisions generally adheres to a systematic sequence of stages:
Identification of Need
The purchasing process initiates when an organization identifies a need or an issue. This recognition may stem from various factors, including the necessity to replace obsolete equipment, enhance operations, or improve technology. Additionally, external influences such as new regulations, shifts in the market, or competitive dynamics may also prompt the identification of a need.
General Requirements Definition
Following the identification of the need, the organization articulates the general requirements for the desired product or service. This stage involves delineating the scope and essential specifications necessary to achieve the organization’s objectives. For instance, if the requirement pertains to new software, the organization will specify the desired features, performance metrics, and compatibility criteria.
Detailed Product Specification
The subsequent phase entails detailing the specific requirements for the product or service. During this stage, technical teams or subject matter experts contribute insights regarding the exact specifications needed. This may encompass dimensions, features, functionalities, and any relevant compliance or quality standards.
Supplier Identification
After establishing product specifications, the organization embarks on identifying potential suppliers. This identification process can be conducted through various avenues, including online research, trade directories, referrals, and industry conferences. The objective is to pinpoint suppliers capable of fulfilling the specified requirements while providing competitive pricing.
Request for Proposals
Organizations then extend invitations to prospective suppliers to submit formal proposals or bids. These proposals detail pricing, delivery terms, service levels, and other critical information. The organization will assess the proposals to ascertain which one aligns best with its needs and offers optimal value.
Supplier Selection
Upon receiving proposals, the organization assesses them according to various criteria, including cost, quality, service, delivery timelines, and historical performance. The decision-making team may engage in negotiations with suppliers to refine terms or modify pricing prior to reaching a final decision.
Order-Routine Specification
Following the selection of a supplier, the organization finalizes the details of the order. This encompasses the agreement on pricing, payment conditions, delivery timelines, and warranty or support provisions. At this stage, the final contract or agreement is formalized.
Post-Purchase Evaluation
Subsequent to the purchase, the organization reviews the performance of the product or service. This stage evaluates whether the product met the anticipated standards and whether the supplier fulfilled their commitments regarding quality, delivery, and service. The insights gathered during this phase can impact future purchasing decisions and the establishment of long-term relationships with suppliers.
Factors Influencing Organizational Buyer Behavior
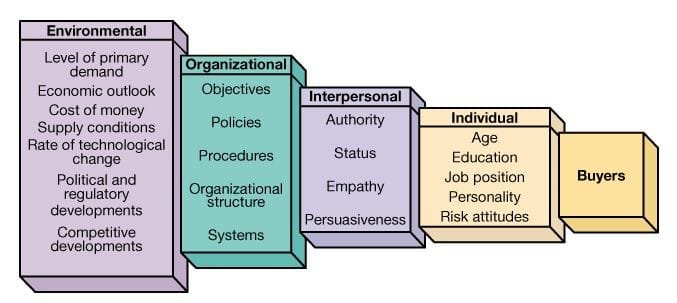
Various elements impact the decisions made by organizational buyers, encompassing both external and internal influences:
Environmental Influences
- Market Dynamics: Economic conditions, industry developments, and technological innovations significantly affect purchasing choices. For instance, during economic recessions, organizations may lean towards more cost-effective options.
- Regulatory Framework: Legal obligations and regulatory standards, such as compliance requirements or environmental regulations, can restrict the types of products and suppliers available to a company.
Organizational Influences
- Strategic Objectives: The overarching business strategy of an organization shapes its purchasing decisions. For example, a company emphasizing innovation may prioritize advanced technological solutions.
- Financial Limitations: Budgetary constraints are crucial in shaping purchasing choices. While cost-effectiveness is vital, organizations must also consider the quality and dependability of the products or services.
Interpersonal and Group Interactions
- Decision-Making Unit (DMU): The purchasing process often involves a collaborative effort among various individuals, including buyers, influencers, decision-makers, and gatekeepers. The interactions within this group can significantly influence the final outcome.
- Conflict and Agreement: Disagreements may surface within the buying group if stakeholders have differing priorities. Effective communication and negotiation are critical for achieving a unified decision.
Individual Influences
- Personal Biases: The preferences or past experiences of individuals within the buying group can sway the decision-making process. For instance, a procurement officer might favor a specific supplier due to previous positive interactions.
- Risk Assessment: Organizational buyers generally exhibit risk-averse behavior and may hesitate to engage with new suppliers or products without substantial proof that the purchase will fulfill their requirements and expectations.
Conclusion
Buyer behavior represents a fundamental element in comprehending the processes through which individuals or organizations arrive at purchasing decisions. This entails a thorough examination of the needs, preferences, and various factors that influence these choices, including cultural, social, personal, and psychological elements. By acquiring a deeper understanding of buyer behavior, companies can more effectively tailor their products, services, and marketing approaches to satisfy customer expectations. Such insights not only facilitate the attraction and retention of customers but also contribute to improved overall business performance and competitiveness. Ultimately, acknowledging and addressing the intricacies of buyer behavior is vital for achieving sustained success in any market.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is Buyer Behavior?
Buyer behavior encompasses the actions and decision-making processes that individuals or organizations engage in when acquiring goods or services. This process includes recognizing a need, making the purchase, and assessing the product or service post-purchase.
2. Why is understanding Buyer Behavior important?
Understanding buyer behavior helps businesses design products, marketing strategies, and customer experiences that meet the needs and preferences of their target audience, leading to increased satisfaction, loyalty, and sales.
3. What factors influence buyer behavior?
Cultural, social, personal, and psychological factors influence buyer behavior.

