The economic environment refers to the nature and direction of the economy in which a firm competes or may compete. In general, firms seek to compete in a relatively stable economy with strong growth potential. It is the most important environmental component of a business. The components of the economic environment are:
- Economic systems
- Economic policies
- Economic conditions
- Economic integration
Table of Contents
Economic System
An economic system is one of the most important components of the economic environment. An economic system refers to the system of production, resource allocation, exchange, distribution, and consumption of goods and services in a country or a given geographical area. It addresses the question of what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce. There are three types of economic systems. They are;
- Market Economy
- Command Economy
- Mixed Economy
Market Economy
A market economy is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production. Under it, resources are allocated through the interaction of free and self-directed market forces which means that what to produce is determined by consumers, how to produce is determined by producers and for whom to produce is determined by the purchasing power of the consumers. Under it, the right to property is allowed. The prices are determined by the interactions of the market demand and supply.
Command Economy
Command economy, also known as the planned economy is an economic system in which the government controls the economy. The government, or the state decides the use and distribution of resources. The government decides what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce. Command economy has only the public sector. For example, the Soviet Union and North Korea’s economic system is a command economy.
Mixed Economy
A mixed economy is an economic system that combines the elements of both the market. It consists of both public and private sectors. Some businesses are owned by private individuals while some businesses are owned and managed by the government. Many decisions are owned by the individuals. But the government also plays a role in the allocation and distribution of resources. Nepal’s economic system is mixed.
Dimensions of an Economy
The dimension of an economy refers to various forces or components that define its structure, functioning, and performance. The dimensions of an economy include economic dimension, socio-economic dimension, industrial and agricultural dimension, and economic development dimension. Each dimension is important because it affects how resources are used and how well the economy is doing. Understanding these dimensions helps people make better decisions about business and government policies.
The Economic dimension
The economic dimension indicates the economic performance of a country. Economic performance may be classified into internal and external economic performance.
- The internal economic performance includes gross domestic product, income distribution, poverty level, personal consumption, saving, debt and credit availability, budget position, inflation, interest rate, and fiscal and monetary policies.
- The external economic performance includes balance of payment, exchange rates, and foreign trade volume.
Socio-economic dimension
The socio-economic dimension looks at how social things (like education, health, and income) and economic things (like jobs and money) affect each other. It shows how people’s lives and the economy are connected. This dimension helps us see problems like poverty and inequality, which can make life harder for many people. Understanding this connection is important for making policies that help improve lives and boost the economy for everyone. The size, distribution, density, growth, age and gender mix, urbanization, and migration of the population are some of the important socioeconomic factors that affect business decisions.
Industrial and agricultural dimension
Industry is related to the production of goods and services. It is the secondary sector of the Nepalese economy. On the other hand, agriculture is the primary sector of the economy. It uses the natural resources directly. The industrial and agricultural dimension of an economy reflects the potential to supply goods and services to consumers and raw materials to industrial units.
Economic development dimension
The pattern of economic development of a country largely depends on the system of national planning. The direction and priority of the development of different sectors and reflected by the development plans.
Analysis of the Economic Dimensions and their Impact on Business
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
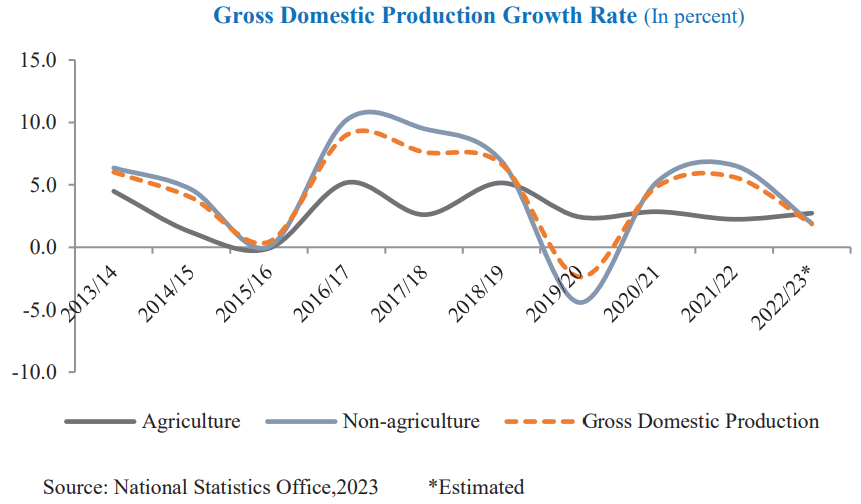
Gross Domestic Product refers to the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced within the geographical boundary of the country over a specified time. It is one of the main indicators used to measure the performance of a country’s economy, It is measured in terms of its size and growth rate.
The latest GDP of Nepal Is 40.91 billion USD.
The GDP growth rate is the most important indicator of the economic health of a country. When the GDP is strong, employment and wage rates increase, as companies demand labor to meet the growing economy. They also have higher confidence to invest more when GDP growth is strong. GDP growth affects the profitability of companies eventually determining the stock price. When GDP growth is very less or the economy goes into a recession, the opposite applies.
GDP per Capita Income
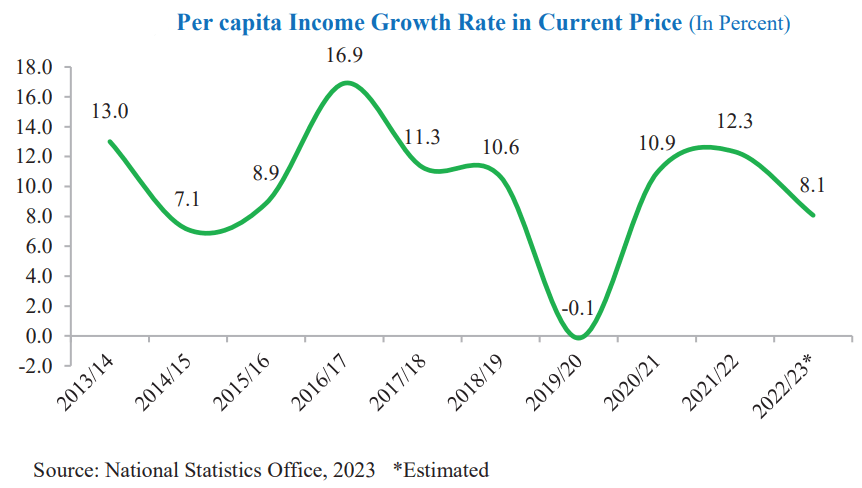
GDP per capita income average income per individual of a country. It is calculated by dividing a country’s GDP by its total population. The PCI indicates the relative purchasing power of the people. GDP per capita income shows living standards as it measures the average incomes of the population.
In the FY 2021/22, the current estimated per capita GDP is Rs. 169,038. It is projected to reach Rs. 182,683 in the current fiscal year, showing an estimated growth of 8.1% in per capita GDP. The GDP per capita income is estimated to increase marginally to US$ 1,410 in the fiscal year 2022/23.
Income Distribution
Income distribution refers to the distribution of the total GDP of a country among its population. It shows who earns what and how much different groups of people make. Some people may earn a lot, while others earn very little. This distribution can affect social stability and economic growth. When income is distributed fairly, it can lead to a happier and more productive society. However, when there is a large gap between the rich and the poor, it can create tension and conflict. Inequality is a signal of a lack of income mobility and opportunity.
Exchange Rate
An exchange rate is the rate between two currencies at which one is exchanged for another. There are two systems of exchange rates.
- In the Fixed Exchange Rate, also called a pegged exchange rate, a currency’s value is fixed against either the value of another single currency, a basket of other currencies, or another measure of value, such as gold.
- In the Floating Exchange Rate system, the price is set by the FOREX market based on supply and demand compared with other currencies. This is in contrast to the fixed exchange rate, in which the government predominantly determines the rate.
Compared to the mid-March of the year 2022, Nepali Rupee has been depreciated by 7.2 percent in mid-March of the year 2023. As of mid-March of the year 2023, buying exchange rate with United States Dollar has been Rs. 131.10 per dollar while such rate was Rs. 122.25 as of mid-March of the year 2022.
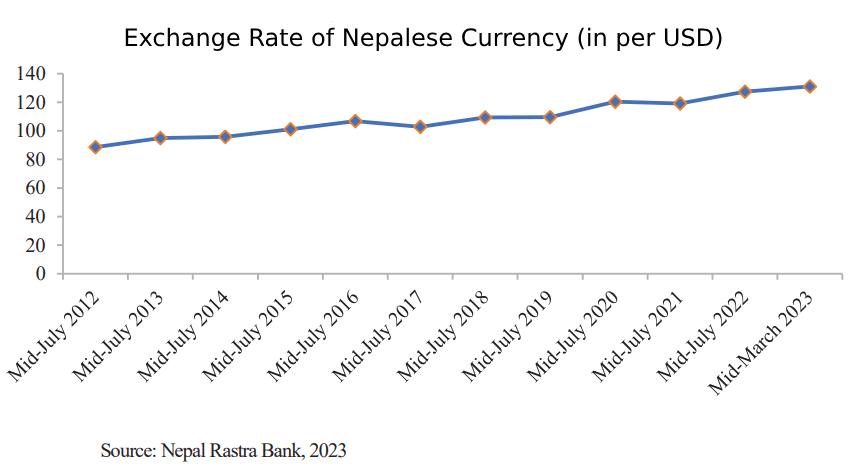
The exchange rate plays an important role for firms that export goods and import raw materials. Depreciation of the domestic currency makes exports cheaper, and exporting firms benefit. However, firms importing raw materials face higher costs of imports. In contrast, an appreciation makes exports more expensive and reduces the competitiveness of exporting firms. However, imports of raw materials become cheaper.
Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate measures the number of people looking for work as a percentage of the total labor force. A lower unemployment rate depicts the economic soundness of a country. When unemployment rates are high, consumers have less money to spend affecting the economy adversely.
As of 2023 the unemployment rate in Nepal is 10.69%.
Consumer Price Index (Inflation)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a measure that reflects the average change in the price of the goods and services that consumers pay over time, such as food, clothing, and housing. It serves as a key indicator of inflation, reflecting how much prices have increased or decreased. When the CPI rises, it indicates that the cost of living is going up, which can reduce the purchasing power of money. This means that consumers may not be able to buy as much with their income, affecting their overall standard of living. In 2022/23 the average inflation rate of Nepal was 7.74%.
Firms generally prefer low and stable inflation because high inflation can lead to increased costs and uncertainty. When inflation rises, the prices of materials, utilities, and labor go up, which raises overall business costs and can reduce profits, especially if companies can’t raise their prices without losing customers. Unexpected inflation makes it even harder for businesses to adjust their pricing and budgets, complicating long-term planning and investment decisions. During challenging times like stagflation—when inflation is high and the economy is stagnant—firms face the dual struggle of rising costs and lower demand, making it difficult to operate effectively.
Poverty
Poverty may be defined as an inability to attain a minimum standard of living. It refers to the condition of the people who cannot meet basic necessities such as food, health, education, shelter, etc. Poverty leads to the unavailability of skilled labor. It also results in low employee productivity due to insufficient training and education. It reduces the demand for products and services. it is also a source of many crimes.
The poverty in rural areas is found to be higher than the urban areas in Nepal. over the years, the poverty in Nepal has been decreasing. The government over the years has been increasing in the social sector. Various employment and income-generating activities are being conducted focusing on the areas and target groups of people living below the poverty line. Micro Enterprises Development Program for Poverty Alleviation was initiated to increase the level of income of poor families in Nepal.
Interest Rates
An interest rate is the amount that a lender charges to individual or business on lending. Bank or other financial institutions are the source of debt financing for the business. Higher interest rates result in higher total business expenses. It can also reduce consumer spending because high rates make it more expensive for consumers to take loans from financial institutions for their spending.
Credit Availability
Credit availability may be defined as the access of the business sector in credit. Higher savings by the people in the financial institutions results in easy credit availability at favorable terms and conditions to businesses.
Business Cycle
The business cycle may be defined as the fluctuations in economic activity that an economy experiences over time. It directly affects the operations of a business firm. The business cycle has four phases. They are:
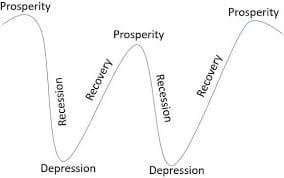
Depression: A depression is a very serious and long-lasting downturn in the economy. Many people lose their jobs, and businesses may close down. People spend less money because they are worried about their finances. This creates a tough situation for families and communities, making life difficult and uncertain.
Recovery: Recovery is when the economy starts to get better after a depression. More people find jobs, and businesses begin to grow again. As people feel more secure, they start to spend money, which helps the economy improve. This phase brings hope and a sense of progress, even though it may take time for everything to fully bounce back.
Prosperity: Prosperity is a time when the economy is doing really well. Most people have jobs, businesses are successful, and people are spending money freely. There is a feeling of confidence and happiness in the community. However, because everyone is buying more, prices can go up, which is called inflation. Overall, prosperity is a time of growth and opportunity.
Recession: A recession is a period when the economy slows down. People may lose jobs, and businesses earn less money. During a recession, people tend to spend less because they are worried about their financial situation. While it’s not as bad as a depression, it can still be a challenging time. However, recessions are often followed by recovery, where things start to improve again.
Taxes
Taxes have direct effect on businesses. Taxes increases the price of their products. This may affect the sales leading to decrease of profit. If the tax rate is low, the stock prices tend to be high due to higher profit.
Monetary Policy
Monetary policy is a macro economic policy. It is concerned with monetary system of a contract. It is how a country’s central bank controls the amount of money in the economy and sets interest rates. The main goals are to keep prices stable, help the economy grow, and reduce unemployment. By changing interest rates and how much money is available to borrow, monetary policy tries to create a healthy economy where people can find jobs and prices don’t rise too quickly.
Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy determines the country’s economic direction. It is the way a government uses its spending and tax policies to influence the economy. It involves decisions about how much money the government spends on services like education, healthcare, and infrastructure, as well as how much it collects in taxes. The main goals of fiscal policy are to promote economic growth, reduce unemployment, and control inflation. By increasing spending or cutting taxes, the government can stimulate the economy, while reducing spending or raising taxes can help cool it down when it’s growing too fast.
Basic Social Indicators for Nepal
Population
Population is the most influencing socio-economic element that affects the business firms. Higher population of a country reflects the business potentiality. However, it is not the sole indicator. It should be analyzed together with other elements.
According to the 2021 census, our population stands at 29,192,480, with a growth rate of just 0.93%, the lowest we’ve seen in 80 years. Interestingly, the Terai region is home to about 53.66% of us, while the hills and mountains account for around 40.24% and 6.09%, respectively. A growing population can be a sign of a thriving market, especially for everyday products like biscuits and soft drinks. With more people, there’s a greater demand for these items, which can lead to exciting opportunities for businesses and the economy as a whole.
Population Density
Population density is the number of people per unit of area, usually quoted per square kilometer. population density if the pattern of the population living in different areas. Some places are sparsely populated and others are densely populated.
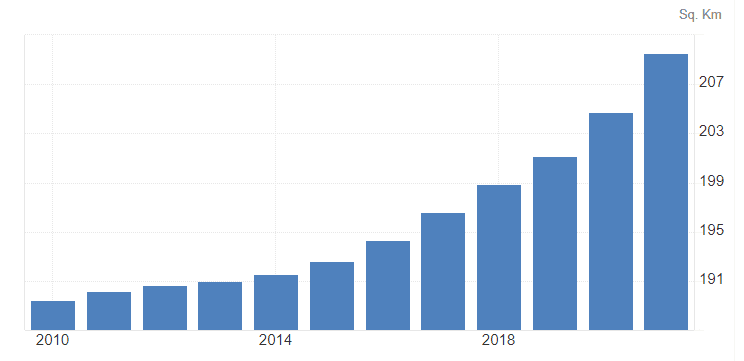
According to World Bank (2021), the population density of Nepal is 210 per square kilometer. Geographically, Nepal is divided into Himalayan, Hilly and Terai region. According to population census 2021, 53.66% of total population lives in the Terai region followed by 40.25% in Hilly region and 6.09% in Himalayan region.
The population in the rural areas stand to be 79% and urban areas 21%. The urban population accounts for 21% of the total population in 2021 compared to 17.1% in 2011. It can be well noticed that there is a significant trend of urbanization in Nepal. The population is concentrating in city and town areas, With the distribution and density of population in Nepal, a number of effects to the business sector may be noticed.
Age and Sex Structure
A business has a great concern over age and sex structure of the population. It is the base of market segmentation to formulate marketing and other strategies by focusing on the target customers as make or female, young or old etc.
According to population censes 2021, 48.9% of the total population are male and 51.1% are female. The combined percentage of the population over 65 years old is approximately 5.6%. The combined percentage of the population between 15 and 64 years old is approximately 86.9%, and the combined percentage of the population below 14 years old is approximately 8.5%.
An Overview of the Fifteenth Economic Development Plan
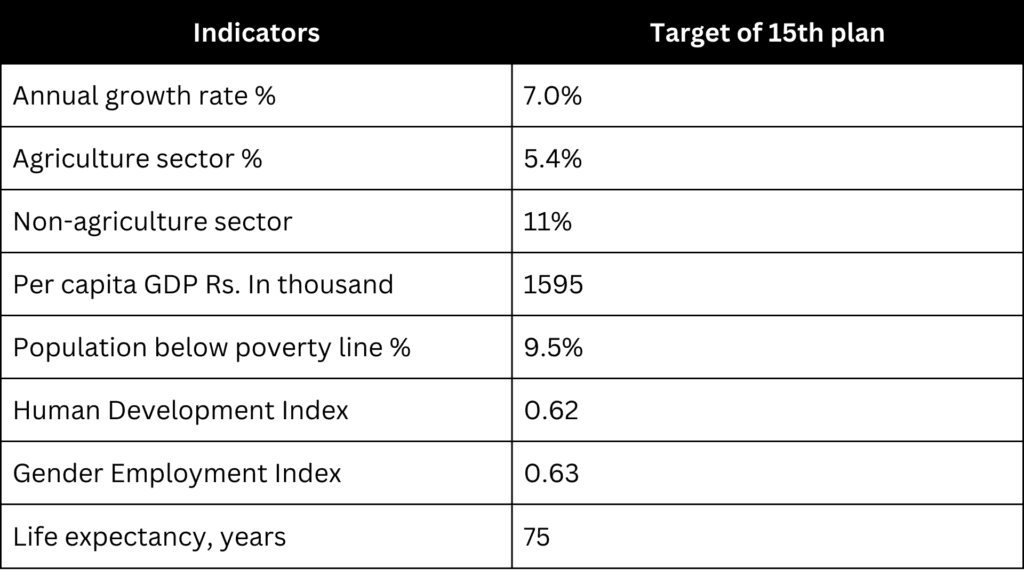
The concept of planned economic development in Nepal was initiated in 1965 with the commencement of first five year plan. The Fifteenth Economic Development Plan (2020-2025) of Nepal is a comprehensive five-year strategy designed to support the country’s growth and progress. With a goal of achieving an average annual growth rate of around 7%, this plan emphasizes key areas such as enhancing infrastructure, modernizing agriculture, strengthening industries, and promoting tourism. It recognizes the vital role of education and skills development, ensuring that everyone has access to opportunities and that the environment is safeguarded. The plan also promotes the integration of technology and encourages collaboration between the government and private sector to optimize resource use.
Vision
To create a prosperous, inclusive, and sustainable economy in Nepal that enhances the quality of life for all citizens, ensuring equitable access to opportunities and resources while promoting environmental sustainability.
Goal
- Achieve an average annual economic growth rate of approximately 7%.
- Improve and expand infrastructure to support economic activities and connectivity.
- Modernize the agricultural sector to increase productivity and food security.
- Boost industrial development and promote entrepreneurship.
- Enhance the tourism sector to attract more visitors and generate revenue.
- Invest in education and skills training to develop a capable workforce.
- Promote social inclusion and reduce inequalities among marginalized groups.
- Foster environmental sustainability and address climate change impacts.
- Encourage the use of technology and innovation in various sectors.
- Strengthen partnerships between the government, private sector, and communities to effectively implement development initiatives.
Strategy
The following are the strategies of the plan to achieve the aforementioned goal.
- Invest in building and upgrading transportation, energy, and communication infrastructure to enhance connectivity and support economic activities.
- Implement modern farming techniques and technologies to increase agricultural productivity and ensure food security.
- Create a favorable environment for industrial growth by providing incentives, improving access to finance, and supporting small and medium enterprises (SMEs).
- Develop tourism infrastructure and promote Nepal as a prime tourist destination by highlighting its natural beauty and cultural heritage.
- Invest in education and vocational training programs to equip the workforce with the necessary skills for various industries.
- Promote sustainable practices across all sectors to protect natural resources and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Encourage the adoption of technology and innovation in agriculture, industry, and services to improve efficiency and productivity.
Conclusion
The economic environment is important for businesses as it shapes how they operate and succeed. In Nepal, the economy is a mix of private and government control, which affects how goods and services are produced and sold. With a GDP of about 40.91 billion USD and an expected increase in average income, Nepal shows promise for growth, but it also faces challenges like inflation and unemployment. The government’s Fifteenth Economic Development Plan aims to improve infrastructure, agriculture, and social equality. Understanding these economic factors is key for businesses to adapt and thrive in Nepal’s changing landscape.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)
What is Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
GDP is the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced within a country over a specified time. It is a key indicator of economic health, influencing employment, investment, and business profitability.
How do exchange rates affect businesses?
Exchange rates impact the cost of exports and imports. A depreciation of the domestic currency makes exports cheaper but increases import costs, while appreciation has the opposite effect.
What role do taxes play in business operations?
Taxes can increase product prices, potentially affecting sales and profits. Lower tax rates may lead to higher stock prices due to increased profitability.

